-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Black screen instead of desktop in RDP session
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Black screen instead of desktop in RDP session
Let's take a look at what to do if you see a black screen instead of a desktop while RDP connecting to a remote host. The problem is especially common in early versions of Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019. Looking ahead, we'll say that the problem is fixable.
What is RDP?
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is a remote desktop protocol developed by Microsoft. It is designed to remotely control a computer over a network. RDP allows users to connect to and control a remote computer or server as if they were directly in front of it.
The protocol is widely used for remote support, server administration, remote working and other similar purposes. RDP is built into Windows operating systems and is available as client and server parts. There are also third-party programs that support RDP to connect to remote desktops, even if they run on other operating systems such as macOS or Linux.
What is RDP for?
RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) is used to remotely access and control a computer or server over a network. Here are some of the main reasons why RDP is used:
- Remote administration: system administrators can use RDP to remotely manage servers without having to be physically present in front of them.
- Remote support: technicians can use RDP to remotely support users by helping them solve problems on their computers.
- Remote working: users can use RDP to access their desktop and files from anywhere they have internet access, allowing them to work remotely.
- Training and Demonstrations: RDP can be used to train users or demonstrate software, allowing them to show their desktop to other users.
- Centralized Management: RDP allows centralized management of multiple computers or servers from a single location.
The tool provides a convenient way to remotely access computers and servers for various purposes.
Causes of the problem
Why does a black screen appear instead of an RDP session?
It is quite problematic to diagnose or categorize, that is, to classify them.
But we will try to do so:
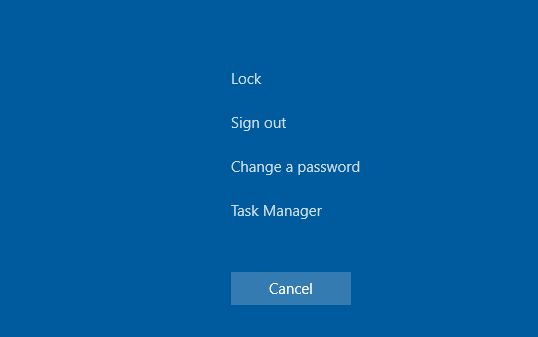
During an RDP session, press CTRL+ALT+END followed by Cancel. This is often the way to get back to the desktop of the RDP session. If it doesn't work, start Task Manager and File Explorer process (File -> Run new task -> explorer.exe -> Ok);
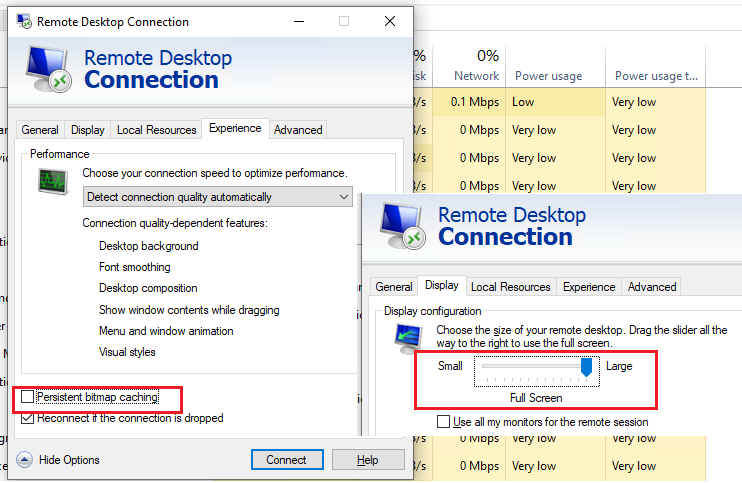
Check that caching is disabled in the RDP client settings (mstsc.exe) (turn off Persistent bitmap caching on the Experience tab) and that the screen resolution is used.
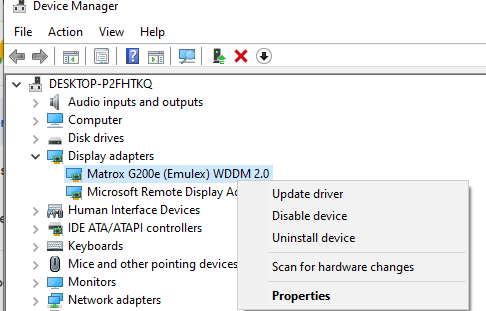
It is supported by the remote host. Check that you have the latest version of video driver on your PC. You can install the drivers manually or set them to update automatically.
Solution to the problem
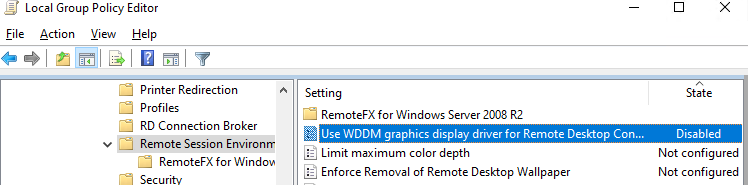
For Windows 10, you need to insert the use of XDDM instead of WDDM. Open the Group Policy Editor gpedit.msc and under Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host -> Remote Session Environment set Use WDDM graphics display driver for Remote Desktop Connections = Disabled. Update Group Policies on the RDP server.
In Windows Server 2016 with RDS sessions timeouts set, sometimes users complain that after connecting to a disconnected session, it did not activate correctly and they saw a black screen. The only way to help here is to terminate the RDP session by the user himself(CTRL+ALT+End -> Sign out), or to force the administrator to terminate the session (similar to the article Failed to complete the required operation when logging in via RDP). Or configure more aggressive settings to disconnect disconnected sessions;
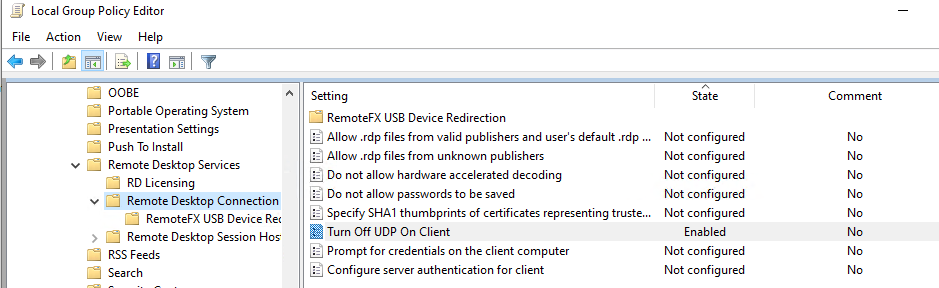
Disable the use of the UDP 3389 protocol for RDP traffic in addition to the standard RDP port TCP 3389 via the Turn off UDP on client parameter on the client (Computer Configuration -> Policies -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Connection Client) or via the registry: reg add "HKLMSOFTWAREPoliciesMicrosoftWindows NTTerminal ServicesClient" /v "fClientDisableUDP" /t REG_DWORD /d 1 /f . To disable the UDP protocol for server-side RDP traffic, configure the GPO setting ...Remote Desktop Session Host -> Connections -> Select RDP transport protocols = Use only TCP.
Other methods
Some more exotic recommendations from Microsoft that do not always help, but can fix the source of the problem:
Check the RDP server, client and all networking equipment between them. They should be configured with the same MTU.
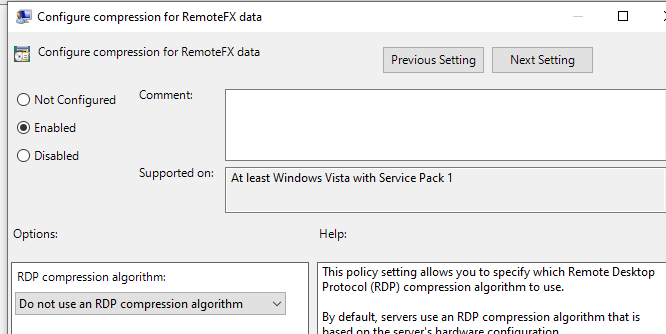
Turn off the option to compress data that is being forwarded in an RDP session via the local GPO editor - Configure compression for RemoteFX data = Do not use an RDP compression algorithm (Computer Configuration -> Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Remote Desktop Services -> Remote Desktop Session Host).
If the RDP black screen issue occurs on Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 1809+. Open Event Viewer and check the Application and Service Logs -> Microsoft -> Windows -> RemoteDesktopService-RdpCoreTS event log.
Check if there are errors like ' Failed GetConnectionProperty' in CUMRDPConnection::QueryProperty at 2884 err=[0x80004001] ', ' Connection doesn't support logon error redirector' in CUMRDPConnection::GetLogonerrorRedirector at 4199 err=[0x80004001].
If available, disable the use of URCP (Universal Rate Control Protocol), which is used to transfer some data between RDP client and server over UDP(MS-RDPEUDP2): reg add "HKLMSOFTWAREMicrosoftTerminal Server Client" /v "UseURCP" /t REG_DWORD /d 0 /f or so New-ItemProperty 'HKLM:SOFTWAREMicrosoftTerminal Server Client' -Name UseURCP -PropertyType DWord -Value 0
Now you know how you can solve this problem.






































