-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
How to restore Grub after Windows installation
- Main
- Knowledge base
- How to restore Grub after Windows installation
If you have two operating systems on your computer, Windows and Linux, and you have upgraded your Windows from 7, 8, or 8.1 to the newest Windows 10, there may be issues with the Grub boot loader when using UEFI Secure Boot. During a system upgrade, Windows 10 will simply erase the Grub bootloader and write its own bootloader in there.
Next, after the system reboots, the user expects to see a Grub operating system selection menu, but instead the new Windows 10 boots. It may seem that there is no way to access Ubuntu or that you can't run Ubuntu alongside Windows 10. But there isn't.
Why restore Grub after installing Windows?
After installing Windows, you may need to restore the Grub boot loader if you have a Dual Boot with Linux. Windows can overwrite the Grub boot loader during installation, which can cause Linux to stop booting. Restoring Grub will allow you to choose your operating system when you start your computer and restore access to Linux.
Restoring Grub
Often experts advise you to install Ubuntu on another disk, but there is a simple solution. You can always use the standard method, for example, using a LiveCD disk. But if you are using UEFI, there is a solution using Windows 10.
Starting CMD
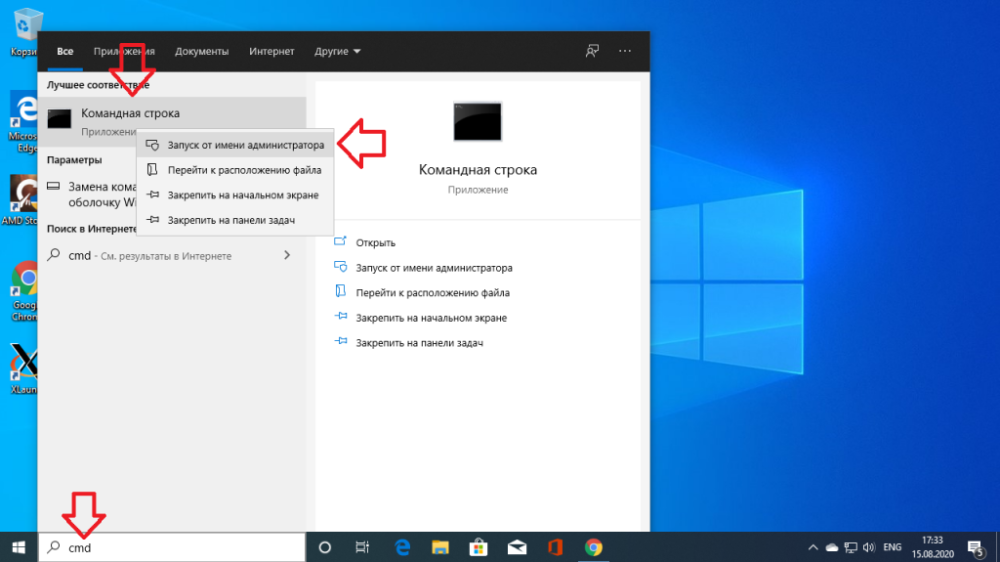
First, click on the search icon in Windows, type cmd there and find the Windows Command Prompt. Right click on it and select Run as administrator:
Connect EFI partition
Next you can try to guess what the name of the Grub boot loader file on the EFI partition is, but you can do the opposite and just look. To mount the EFI partition run diskpart. To do this run:
$ diskpartThen bring up a list of available disks:
$ list diskSelect as active the disk where Windows 10 is installed and where the EFI partition is currently located:
$ sel disk 0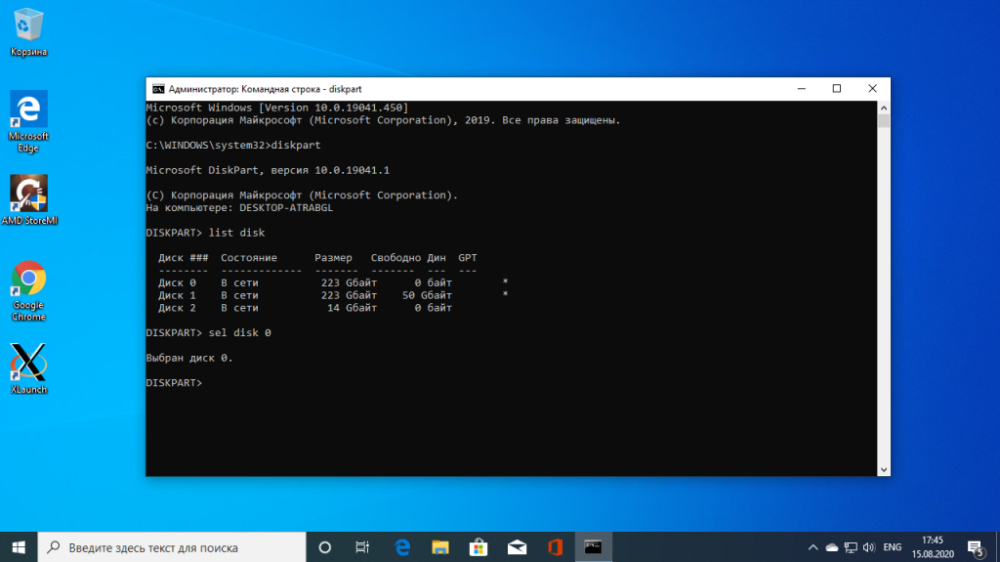
Bring up a list of partitions on the disk:
$ list volLocate the EFI partition, it is usually formatted to the FAT file system and takes up about 100 megabytes of space. In this case, it is volume 2:
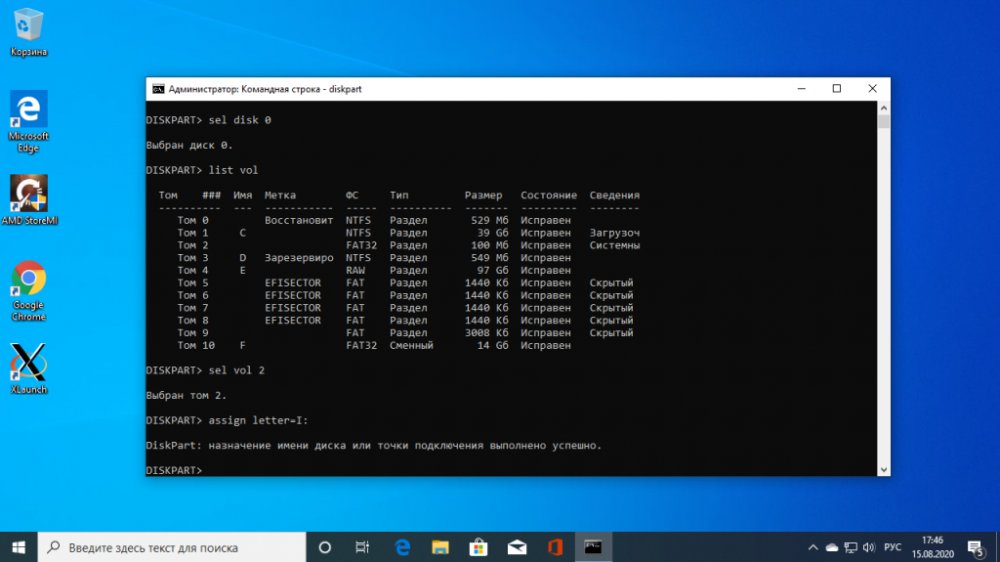
This partition needs to be assigned a letter. To do this, perform:
$ sel vol 2
$ assign letter=I:
Find bootloader
Now you need to find the boot loader file on the EFI partition. But you can't open this partition in Explorer, you need to use the command line only. Close DiskPart and execute:
$ cd /d I:Then use the dir command to find the Grub bootloader. For example:
$ dir EFIUbuntu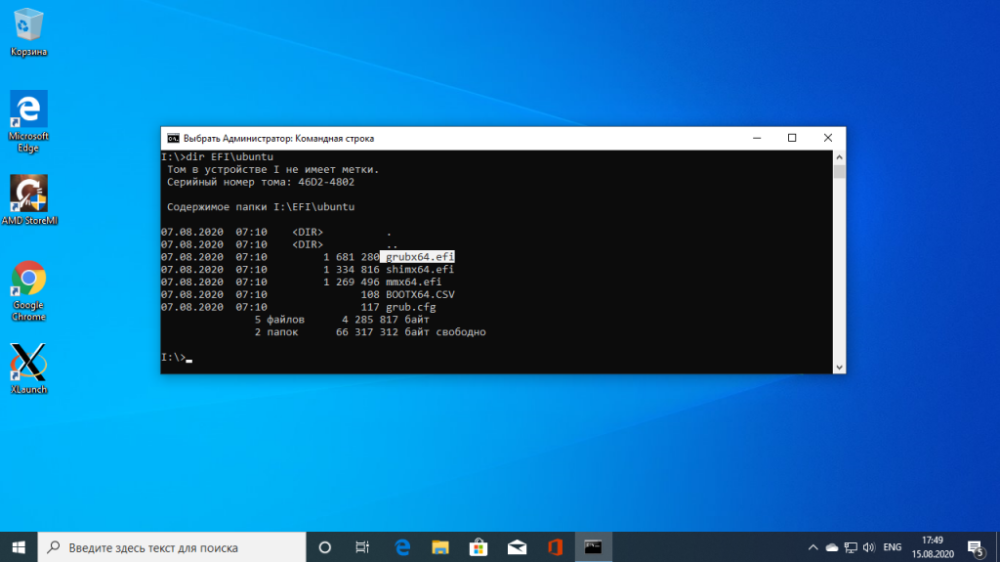
There is a file grubx64.efi here. This is it. The bootloader may be called differently in other distributions, which is why I told you how to look it up.
Restoring GRUB
Now copy and run this command:
bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path EFIubuntugrubx64.efiYou won't have to enter a password if you have administrator privileges and the program should work fine. This command will write back the Grub bootloader instead of the Windows 10 bootloader.
If the command returned an error, you can roll back the changes with this command:
$ bcdedit /deletevalue {bootmgr} path EFIubuntugrubx64.efiYou can then enable the Windows 10 bootloader:
$ bcdedit /set {bootmgr} path EFIMicrosoftBootootmgfw.efiRestart your computer and you will see the familiar Grub on the screen. This completes the Grub recovery process.
Why recovery fails?
There are several reasons why restoring Grub can be difficult after Windows installation. Here are some of the possible reasons:
- Bootloader Overwriting: When installing Windows, especially on the same partition where Linux is installed, Windows may overwrite the Grub bootloader with its own bootloader, causing Grub to no longer be available.
- UEFI and Secure Boot: On computers with UEFI and Secure Boot enabled, additional configuration may be required to restore Grub after Windows installation.
- Different partitions and disks: If different operating systems are installed on different partitions or disks, this can also affect the way Grub is recovered.
- Incorrect recovery: sometimes errors or incorrect commands may occur while trying to recover Grub, causing the recovery procedure to fail.
- Windows updates: after Windows updates, there may be problems with the Grub bootloader due to changes in the system.
To successfully restore Grub after Windows installation, it is recommended to use specialized instructions for your specific configuration and Linux distribution






































