-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Saving a file in Nano Linux
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Saving a file in Nano Linux
The text editor called Nano for Linux is considered one of the most common among beginners. It has the advantage of being able to edit configuration files without any problems, it is also easy to use, and it is available from most distributors. In this tutorial we will tell you how to save a file in Nano. if you have already made changes to the configuration file.
What is Nano for Linux
Nano is a simple command-line text editor that is often used in Linux distributions. It provides basic text editing functions such as insertion, deletion, search and replace, and supports various programming languages thanks to syntax highlighting.
It has a simple interface and control keys, making it accessible to command line novices. It is one of the most popular text editors in Linux due to its ease of use. To start Nano, just type the command "nano" in the terminal and it will open a text file in the Nano editor where you can make changes and save files.
How to save changes in Nano
There are several ways to save. Let's look at each one in detail.
Normal saving
The easiest way is to press the keyboard shortcut Ctrl+O. once all changes to the file have been made to save them. At the bottom of the program, you can see all the hotkey shortcuts you need to use the utility. This part of the program lists all the shortcuts that can help you in your work.
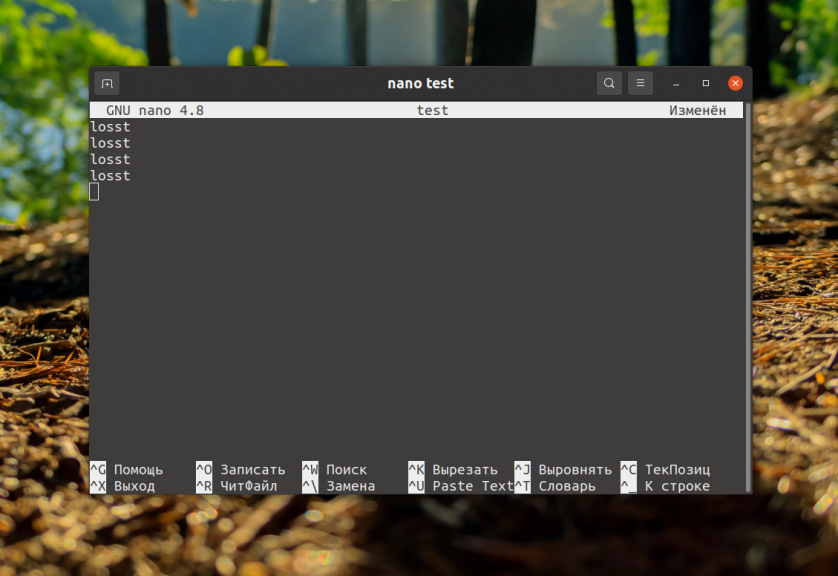
Immediately after pressing the keys, the editor will ask you to enter the name of the file to save:
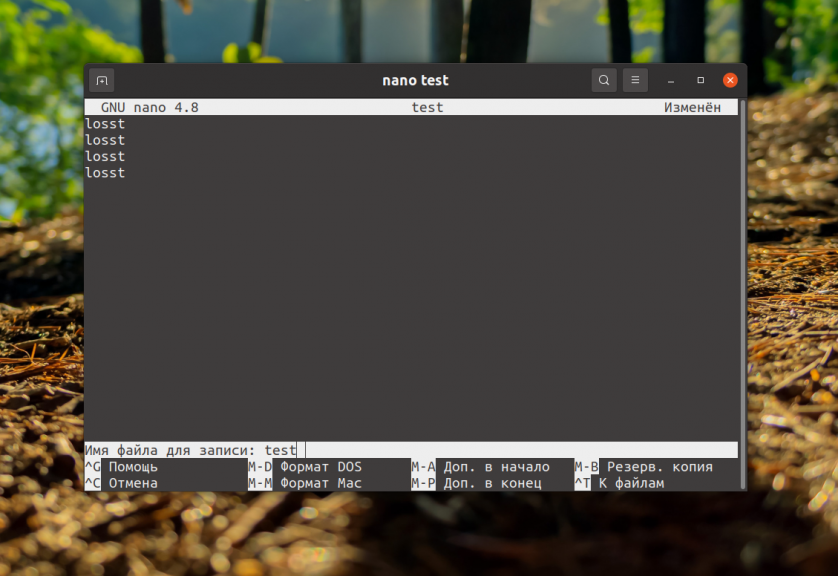
Once you are done, press Enter. To return to the editing window press Ctrl+X. Next, the program will inform you that the file has been successfully saved.
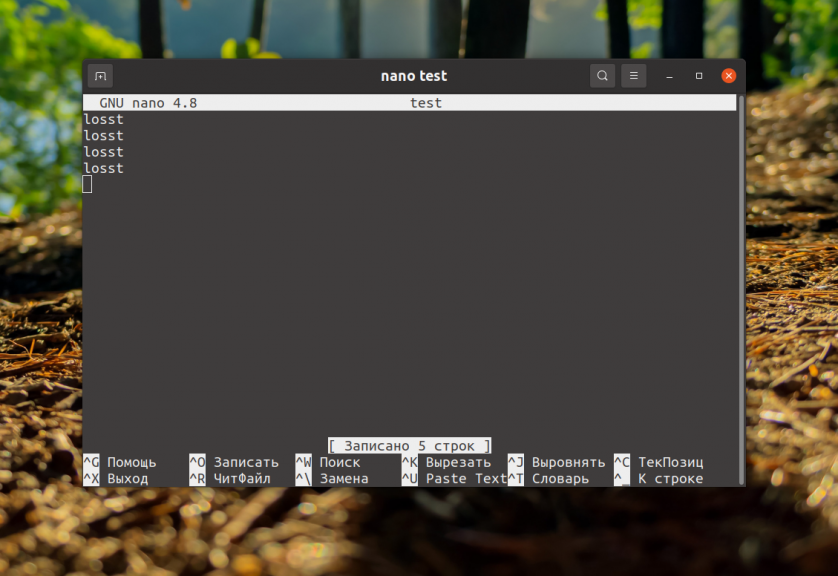
At this point you can close the editor by pressing Ctrl+X.
Saving without write access
Let's also consider the case when you need to save data to a file that belongs to another user or superuser, and this record has no access or permission. In such a case, the user will see: "Write error /filename/file name: Access denied":
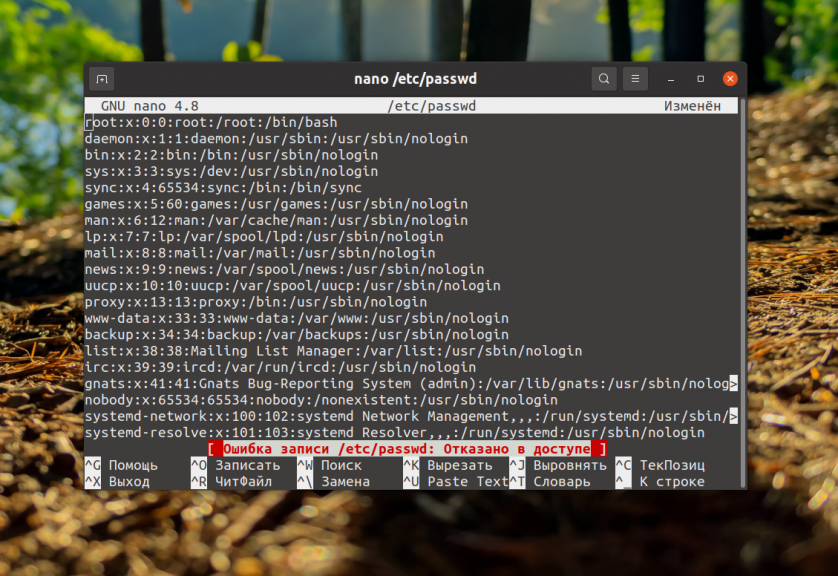
How to solve the problem? The easiest way is to close the editor(Ctrl+X) without saving the changes. The answer to the question is No:
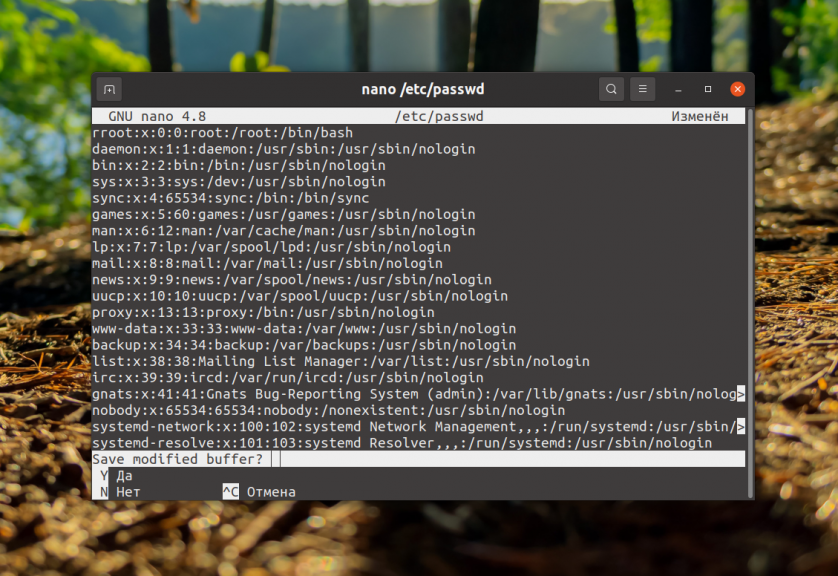
After you have done this, you can run the editor as a superuser:
$ sudo nano /etc/passwdNext, you can write the data to a file. If the changes cannot be lost, at the file name prompt, specify the path to the new file in your home directory, e.g. ~/temp_passwd:
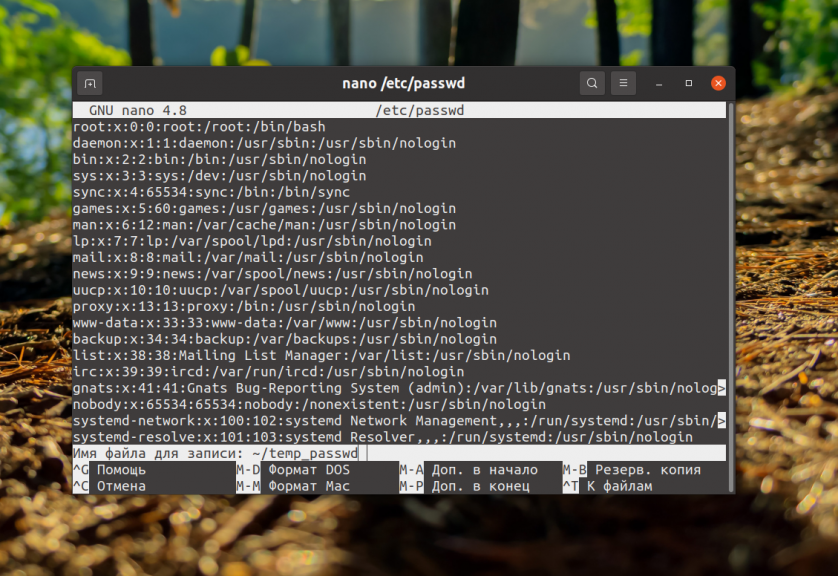
However, if you try to save data to a file belonging to another user or superuser to which you do not have access (for example, configuration files in the /etc directory), you will get the error: "Error writing /filename/file name: Access denied":
The easiest thing to do is to close the editor by pressing Ctrl+X without saving the changes. You should answer the editor's question about saving the buffer with No:
And then open the editor as a super user:
$ sudo nano /etc/passwdAfter that you will be able to write data to the file as described above. If you don't want to lose the changes, you can specify the path to the new file in your home directory during the file name request, e.g. ~/temp_passwd:
The file will then be saved there, where you can then easily move it to replace the old one with the mv command using sudo:
$ sudo mv ~/temp_passwd /etc/passwdRemember that all system files should be edited as superuser.
Advantages of Nano
Has several advantages that make it a popular text editor for Linux users:
- Ease of use: it has a simple interface and control keys, making it ideal for those who are new to the command line. No need to memorize complicated keyboard shortcuts like other text editors.
- Small size and fast loading: is light in bulk and starts up quickly, making it a great choice for quick file editing on the server or in the terminal.
- Syntax highlighting: supports syntax highlighting for various programming languages, making it easy to read and edit code.
- Ability to work on remote servers: works on the command line, it can be used to edit files on remote servers via SSH without the need for a GUI.
- File saving and uploading capability: allows you to easily save and upload files, as well as perform other basic text editing operations.
- Most Linux distributions come with Nano by default: Linux users can find Nano installed on most distributions without having to install it separately.
These advantages make Nano a popular choice for those looking for a simple and efficient text editor in a Linux environment.






































