-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
IPv4 and IPv6: What are they and what is the difference?
- Main
- Knowledge base
- IPv4 and IPv6: What are they and what is the difference?
Internet Protocol is the most important communication protocol in the Internet Protocol Suite, which is used to route and address packets for network devices such as computers, laptops on a single network or on a number of interconnected networks. There are currently two versions of the Internet Protocol: IPv4 and IPv6 . What do IPv4 and IPv6 mean? How can I tell the difference between IPv6 and IPv4? Next we will tell you in detail about the main differences.
IPv4 - what is it?
This is the fourth version of IP, which establishes the rules for the functioning of computer networks on the principle of packet exchange. A distinctive feature of this version is that it uses a 32-bit address scheme, allowing you to store 2^32 addresses (4.19 billion addresses). When a device (computer, switch, or any other equipment) connects to the Internet and accesses the global network, it is assigned a unique IP address. It can be, for example, 192.149.252.76 or another set of digits.
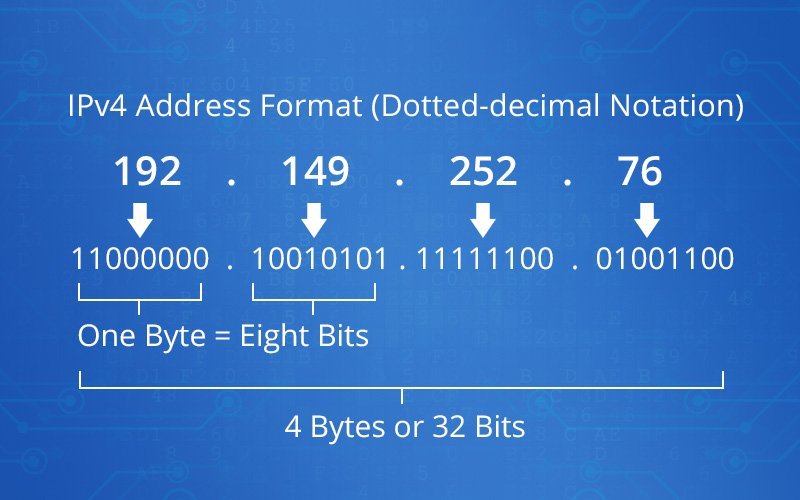
Let's note the main features of this version of the protocol:
1. Protocol without establishing a connection.
2. Allows the creation of a simple virtual communication layer on a variety of devices
3. does not require a large amount of memory.
4. Supported by millions of devices.
5. Offers video libraries and conferencing.
However, shortly after the appearance and launch of IPv4 its main disadvantages were revealed - first of all, the lack of scalability. Also important is the fact that the protocol requires add-ons like ICMP and ARP to work properly. As over time the requirements for the Internet became more and more, there was a need for a new and more advanced communication protocol. So efforts were directed to the development of IPv6. A new version emerged that meets the more stringent requirements better than the previous version.
IPv6 - what is it?
IPv6 was deployed in 1999. One of the reasons for its introduction was the extremely high demand for IP addresses. That is, by this time IP addresses on IPv4 banal became insufficient to meet the basic requirements. Here it is worth noting that the IP-level of the TCP/IP protocol stack is considered the most important part of the entire architecture of the global network.
So together with IPv6 even more addresses became available, covering the current level of demand. IPv6 is a 128-bit IP address that supports 2^128 Internet addresses. Using IPv6 solves the problem of limited network address resources, plus removes barriers to many access devices. An IPv6 address can be written as 3ffe: 1900: fe21: 4545: 0000: 0000: 0000: 0000: 0000: 0000: 0000.

The main features of the new version of the protocol are:
- Hierarchical addressing and routing infrastructure.
- Stateful and non-stateful configuration.
- Quality of Service (QoS) support.
- An ideal protocol for communicating with neighboring nodes.
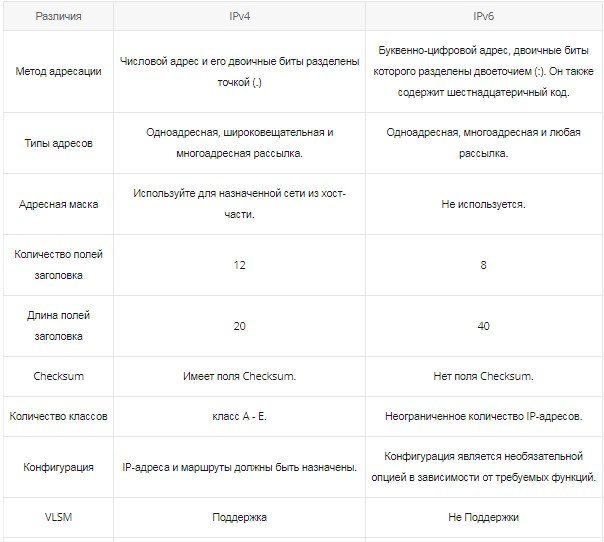
We can say that IPv4 and IPv6 are completely identical in their purpose, as both protocols provide identification of computers and other equipment connected to the WAN. But they work in different ways. What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
Based on the features of the two versions of the protocol and the above in general, we can note the key differences between them. They are as follows:
The 128 bits in an IPv6 address are represented as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks with colons between these blocks. For example, 2dfc:0:0:0:0:0217:cbff:fe8c:0. When IPv4 is written as four decimal numbers (0 through 255) separated by dots. Subnet masks are indicated through fractions - 192.168.0.0.0/16.
IPv4 uses broadcast addresses to transmit appropriate packets, IPv6 multicast groups.
IPv4 uses 0.0.0.0.0 as an undefined address, and 127.0.0.1 to create a loopback address. IPv6 uses :: and ::1 for this purpose.
IPv4 uses globally unique public addresses for traffic and "private" addresses, IPv6 globally unique unicast addresses and local addresses (FD00::/8).
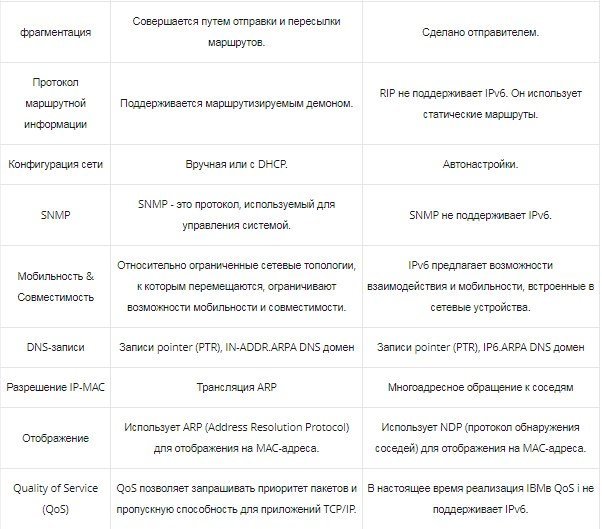
In the end, IPv6 is simply better than the past version. In what ways? For example, the protocol provides more efficient routing without packet fragmentation. Plus, this version includes QoS technology that can identify delay-sensitive packets.
Improved header structure reduces processing time loss, and address autoconfiguration is available to simplify network administration.
Which protocol is faster and more secure?
We can't say that IPv6 is safer than IPv4. In this respect they are the same. But after the launch of IPv6, it became possible to encrypt Internet traffic using the IPSec encryption standard. It is less common than SSL, but still prevents the contents of traffic from being read when it is intercepted. Encryption can be provided only with the help of special equipment, which costs a lot of money. To be fair, IPSec can also be implemented on IPv4.
Another popular question is which version is faster. Here we emphasize that you will not feel a serious difference in the speed of the Internet with IPv6 and IPv4. IPv6 has a simple format, but during the transition, some methods like IPv6 tunnels will create additional delay in converting requests to IPv4. So you won't experience a speed boost with IPv6, nor will you experience a slowdown in Internet speeds if you use IPv4.
Why don't everyone switch to IPv6?
The main issue is financial. Switching to IPv6 requires a complete replacement of all network equipment (switches, etc.), designed to work with IPv4. That's why not everyone considers it rational to change anything. In addition, dynamic IP-addresses slow down the transition to the new protocol. This is one of the measures to combat the lack of addresses. After connecting and disconnecting from the Internet, a user with a dynamic IP address frees it and makes it available to other users. But this does not mean that IPv6 is not in use today. According to some providers in the United States, about half of subscribers have switched to using this version of the protocol. Today it is actively used in parallel with the previous version.






































