-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
What is LTS
- Main
- Knowledge base
- What is LTS
If you use Ubuntu distributions, sooner or later you will come across such a term as LTS. Experienced Linux users, in particular Ubuntu distribution owners, are familiar with and know what LTS is. But novice users may have some difficulties when they encounter this term for the first time. To avoid this, in this article we will tell you what LTS is in the Linux operating system environment, in particular in Ubuntu.
What is an LTS release?
To begin with, it is worth deciphering the term LTS, and it stands for Long-Term Support. What this actually means is that an application or operating system will be updated and receive security updates and sometimes even functionality updates for an extended period of time, much longer than normal.
LTS distributions are considered to be extremely reliable and stable, because they are thoroughly tested and proven before they go into release. And it's worth noting here that users of the LTS version will not necessarily receive functionality updates, but security updates and bug fixes will be guaranteed.
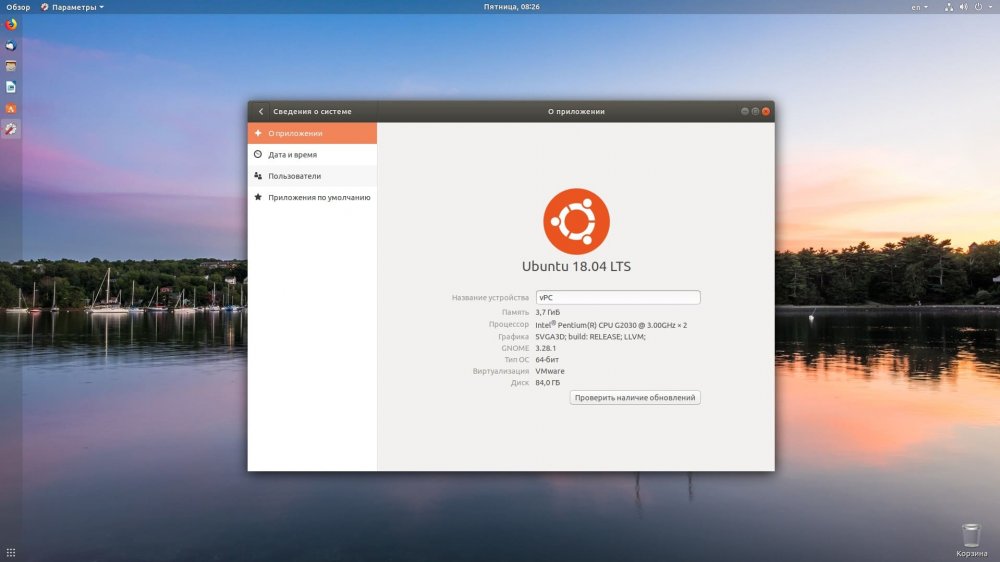
This means that there are reasons to use LTS in production, business and enterprises because the system will be supported for several years and no critical changes will be made to it. An LTS release is typically supported for 3-5 years, where in a non-LTS release, where the latest functionality and tools are the most recent, support lasts only six months, nine months at most.
Advantages of an LTS release:
- Programs are security updated over a long period of time;
- are thoroughly tested before release;
- no major changes that break compatibility;
- the user will have plenty of time to prepare for the transition to the next LTS release.
Minuses of LTS releases:
- the newest features and functions are missing;
- no support for the newest hardware;
- lacking the latest versions of programs.
Ubuntu is one of the most popular distributions of the Linux operating system, which can be either in LTS or non-LTS release. For a better understanding, let's tell you about its main features.
What is Ubuntu LTS?
The creator of Ubuntu releases non-LTS with a set periodicity - once every six months. In LTS, a release occurs every two years.This has been the case since 2006. One of the latest LTS releases is Ubuntu 20.04.It is scheduled to be supported until April 2025. And non-LTS releases are only supported for nine months.
You will always see the LTS symbols in the name of the LTS release of Ubuntu. For that, you can go to the official Ubuntu website and you will find the LTS releases. Look at Ubuntu 16.04 - it came out in 2016 and will be supported until 2021. The exact same versions work the same way.






































