-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
What are services in Linux
- Main
- Knowledge base
- What are services in Linux
Services in Linux are programs that run in the background and provide certain functions or services to the system or users. They run independently of user interaction and are started at operating system startup.
What are services in Linux for?
Linux services can include various services such as database servers (MySQL, PostgreSQL), web servers (Apache, Nginx), mail servers (Postfix, Sendmail), DNS servers (BIND), DHCP servers (ISC DHCP), VPN servers (OpenVPN) and many others.
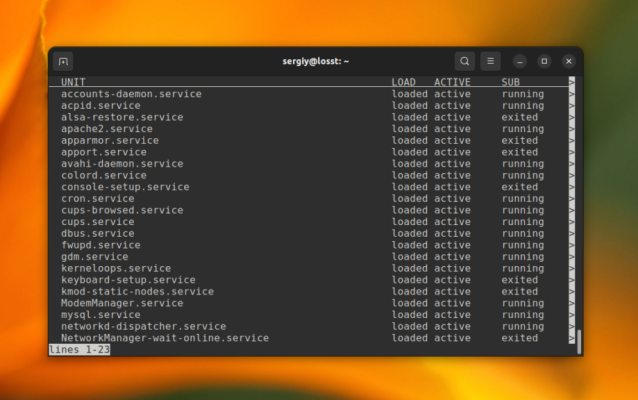
Services in Linux play an important role in ensuring the functionality and stability of the operating system. They provide various services and features to the system and users. Here are a few reasons why services in Linux are essential:
- Providing network services: web servers (Apache, Nginx), mail servers (Postfix, Sendmail), DNS servers (e.g., BIND), and DHCP servers (ISC DHCP), allow users to exchange information and communicate with each other over the network.
- Data processing and storage: services such as database servers (MySQL, PostgreSQL) provide the ability to store and display data, as well as perform queries and data processing on the server.
- System Management: responsible for low-level tasks such as log management, network configuration, power management, and other aspects of the Linux operating system.
These services can be started automatically at system startup and can also be managed using the"systemd" utility. This allows you to control the starting, stopping, restarting, and configuration management of the services. Linux distributions may also provide additional tools for managing services, such as systemctl in systemd or service in SysV.
How to start services in Linux
You can use different methods to start a service in Linux, depending on the distribution and system manager you are using.
Here are some common ways to start services.
1. Using the systemctl utility: most modern Linux distributions use systemd as the system manager. To start a service using systemctl, use the following command:
sudo systemctl start <service_name>Here <service_name> is replaced by the name of the specific service you want to start.
2. Using the service utility: some Linux distributions, especially those that use System V init, can use the service command to manage services. For example, to start the Apache service using service, use the following command:
sudo service apache2 startDepending on your Linux distribution, you may also have other ways to start services. For example, for distributions that use Upstart, you can use the start command to start the service.
Apply the discount by inserting the promo code in the special field at checkout:






































