-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Deleting the Git branch
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Deleting the Git branch
In order to ensure the development of different software versions, branches are implemented here. They are used to develop new functionality in the utility. If the product is developed by a team, each developer can work on a certain functionality in a separate branch.
How to delete
Before deleting a branch, let's see what we have. To view local, use the command in the repository folder:
$ git branch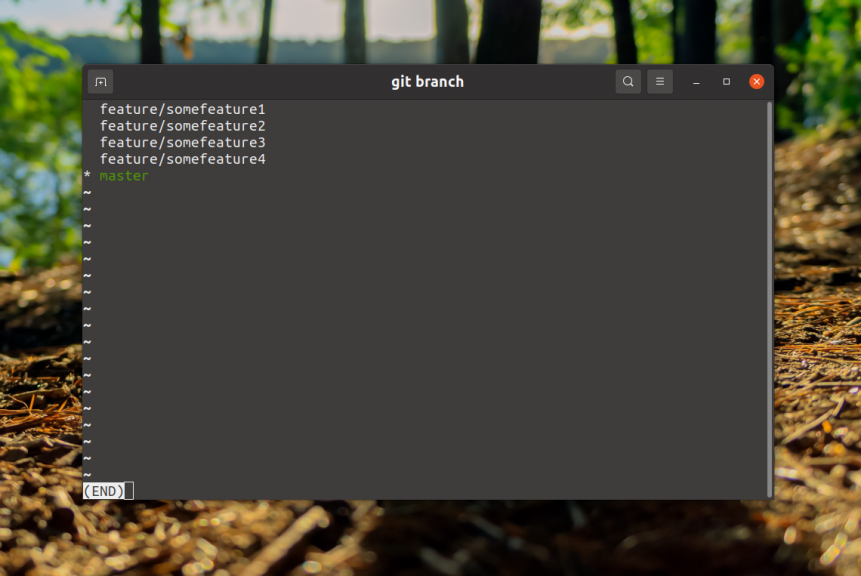
The command displays a list of local ones, with the current one highlighted in green and an asterisk. To remove it, use the same branch command with the -d option. For example, to remove feature/somefeature1 run this command
$ git branch -d feature/somefeature1As an option:
$ git branch --delete feature/somefeature1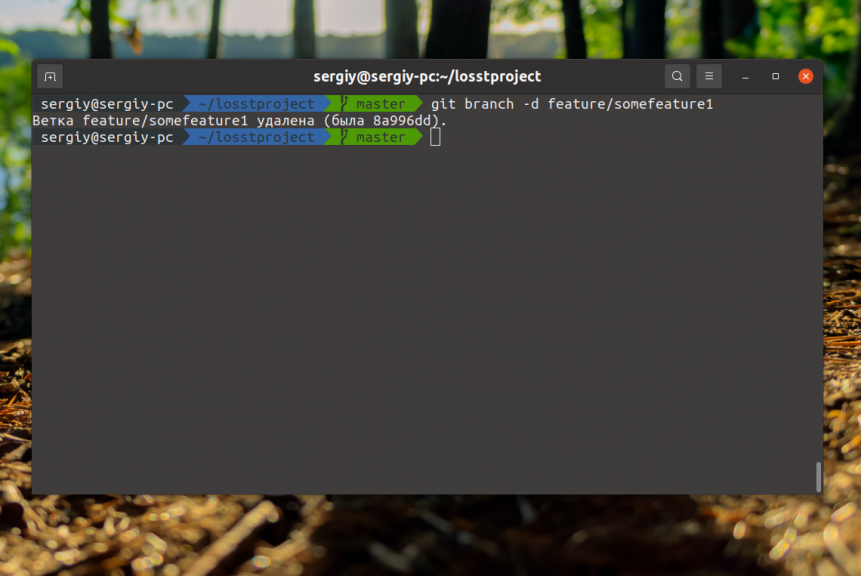
If this branch has uncommitted changes or commits that have not been sent to the server, the program may refuse to delete it. To delete it, use the -D option:
$ git branch -D feature/somefeature1$ git branch --delete --force feature/somefeature1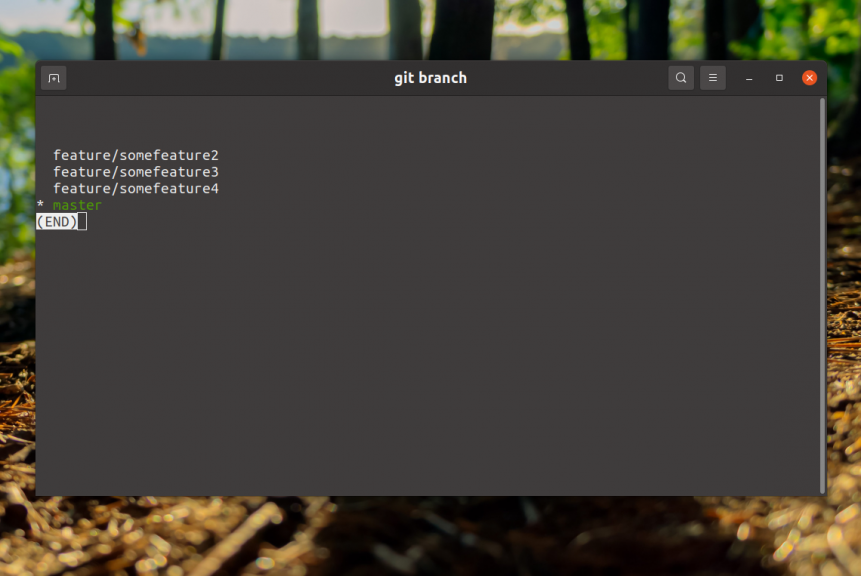
The branch is deleted, if you check the list of local branches again, this branch will no longer be there:
Next, let's understand how the deletion of a deleted branch is performed. In this case, the branch is deleted only locally, but if it has already been sent to the deleted repository, it is still there.
How to delete a deleted branch
How to remove it from a remote repository? First of all, you need to get the list and all updates from the added deleted repositories.
Executing:
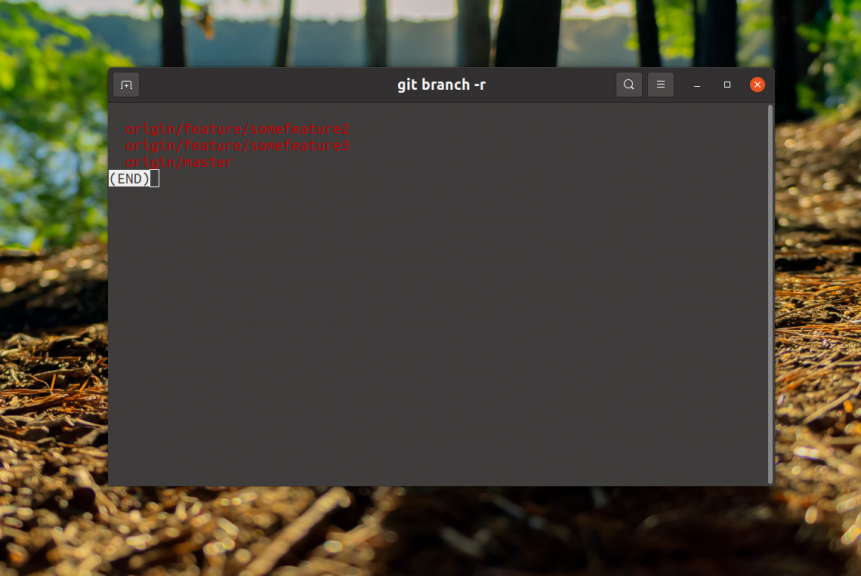
$ git pullTo see the deleted ones you need to run this command in the git repository folder:
$ git branch -r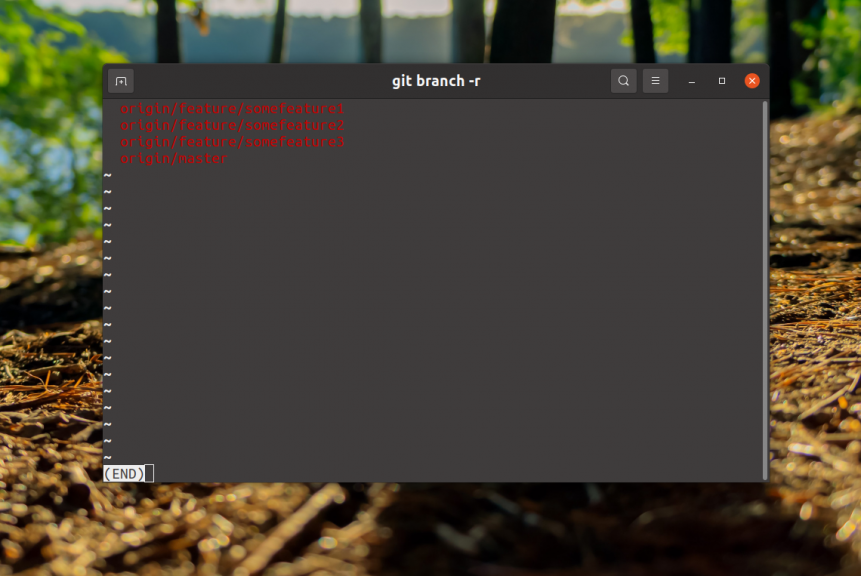
Here are the ones marked in red and in front of the name of each of them is the source where it is. In this case it is origin. To delete a deleted one, the push command with the --delete option is used, for example, for the same feature/somefeature1 the command would look like this:
$ git push origin --delete feature/somefeature1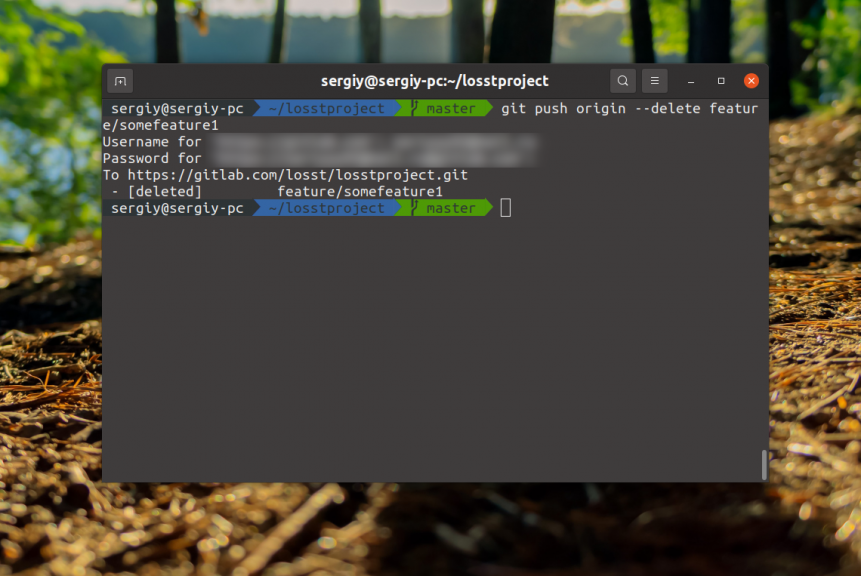
It is now missing from the repository.
The commands that allow deleting a deleted is there, and there is also a simplified syntax. Instead of the --delete option, specify a colon before the name.
For example:
$ git push origin :feature/somefeature1Such a command will also work. If you want to remove all deleted branches that do not exist locally, use the command:
$ git push --prune origin





































