-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
How to view Linux packages
- Main
- Knowledge base
- How to view Linux packages
In the Linux operating system, packages are special archives that contain software and information about installing and configuring it. Each package is a set of files associated with a specific program or library.
What are packages
Packages in Linux are used to manage the installation, uninstallation, and upgrade of software. When you install a program, the package manager downloads the appropriate package from the repository, unzips it and copies the files to your computer, and performs the necessary customizations.
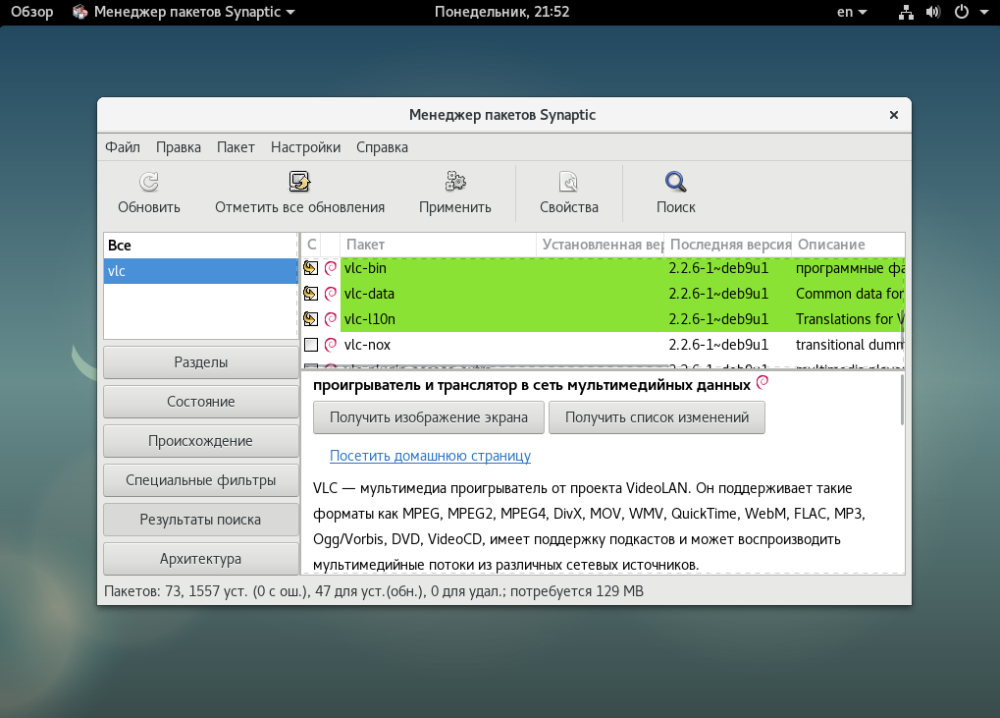
They have the extension .rpm (for Red Hat-based distributions such as Fedora and CentOS) or .deb (for Debian-based distributions such as Ubuntu and Linux Mint). There are many different package managers, such as apt, yum, and pacman, each of which uses its own package format.
What they are for
Packages allow you to easily manage the installation, upgrade, and uninstallation of programs on your system. In Linux, there are several package formats such as RPM (Red Hat Package Manager), DEB (Debian Package), TGZ (tarball) and others.
They also contain metadata such as the name, version and description of the program, as well as author and license information. This metadata allows you to manage software dependencies and updates.
Linux packages can be installed from official Linux distribution repositories or from third-party sources. You can also create your own packages to install on other Linux systems.
Viewing packages in different distributions
In most Linux distributions, you can view the list of installed packages using a special command in the terminal.
Debian and Ubuntu
In Debian and Ubuntu you can use the dpkg-query command:
dpkg-query -lThis command will output a complete list of installed packages in "package, version, description" format.
Fedora, CentOS
In Fedora, CentOS and other distributions that use the yum or dnf package management utility, you can use the command:
yum list installedAlternatively
dnf list installedThese commands will output a list of installed packages with their versions and descriptions.
Arch Linux
In Arch Linux and its derivatives, you can use the command:
pacman -QThis command will list all installed packages.
OpenSUSE
In OpenSUSE you can use the command:
zypper search -installed-onlyThis will list all installed packages.
Slackware
In Slackware you can use the command:
ls /var/log/packages/Now you know how to see the list of packages in each distribution.
Apply the discount by inserting the promo code in the special field at checkout:






































