-
Russia8 (800) 707-83-77
-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Installing certificates in Ubuntu OS
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Installing certificates in Ubuntu OS
In the last article we explained what certificates are in Ubuntu and what tasks they perform. In this article we will talk about how to install certificates, in particular how to install them in the operating system.
Installation in the OS
If you want to use signed certificates to enable HTTPS support on a Web server, then open that Web site in a browser or query it on the command line, the system will give you an SSL error.
It will say that this certificate is not trusted and connecting to this site may not be secure.
curl -I https://localhost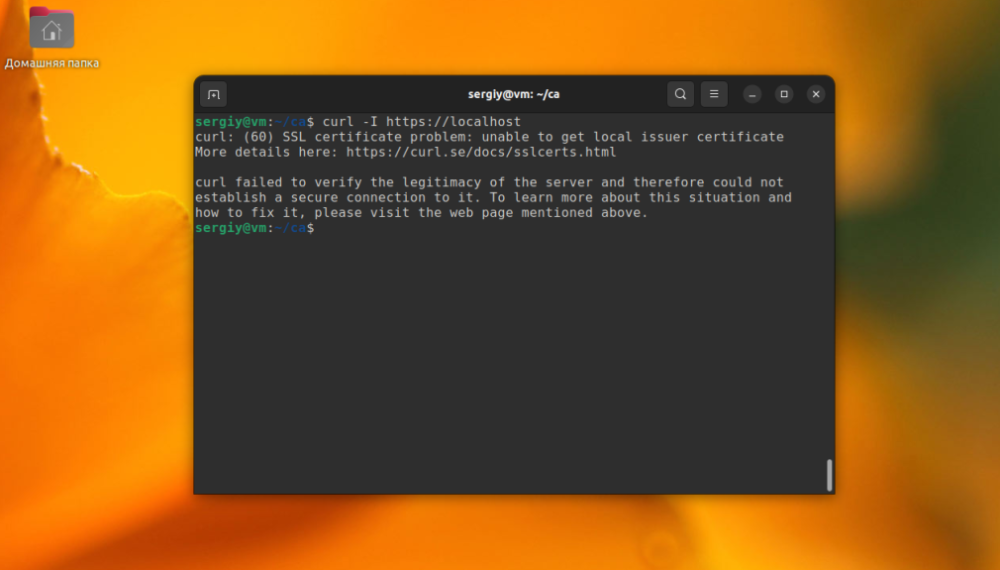
For a certificate to be considered trusted, the OS must add the root certificate of the CA that signed the certificate to the trusted list. If the certificate is self-signed, you can add the certificate itself to the trusted list.
You already have a ca.crt. certificate, but how can you make the OS treat it as valid? To do this, copy it to the /usr/local/share/ca-certificates folder:
cp ./ca.crt /usr/local/share/ca-certificates/losstca.crtThe next thing to do is to execute the command:
sudo update-ca-certificates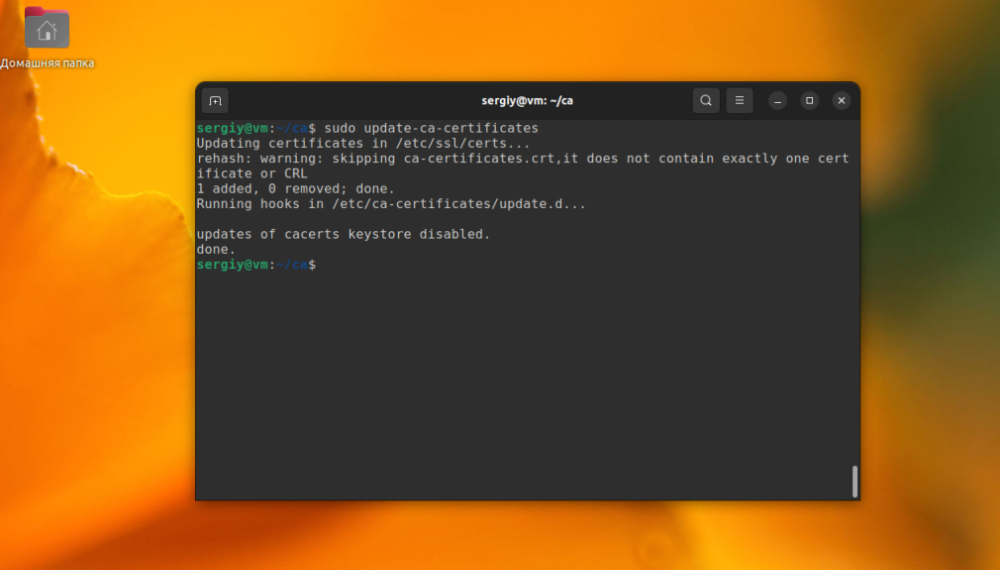
Then you need to verify that the system recognizes the certificate as trusted by running the curl command:
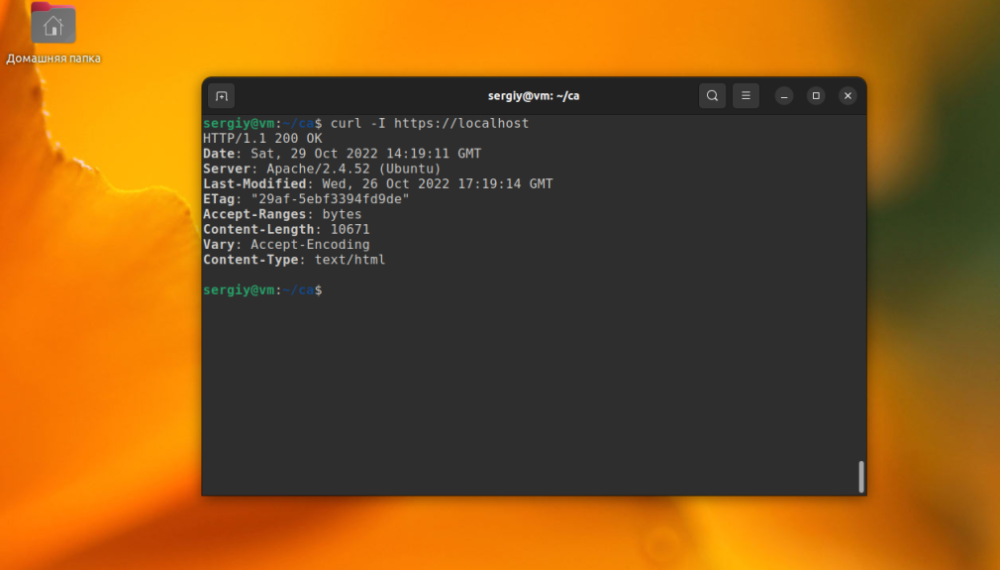
However, this method is appropriate when programs use the system's trusted certificate store. Browsers (Firefox and Google Chrome) have their own certificate stores and do not use the system store. Each browser needs to import certificates separately.
Otherwise, you will get an error like this:
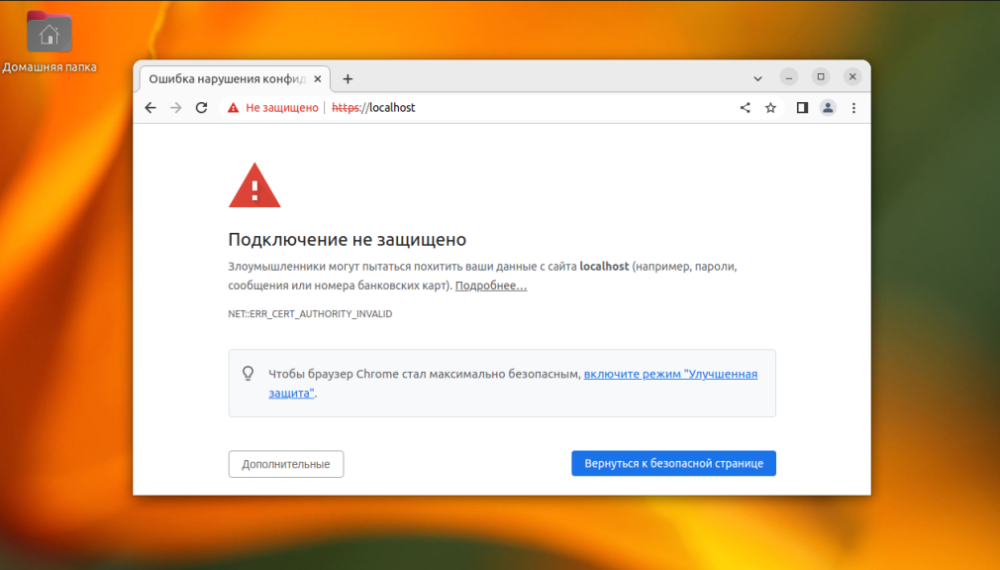
Chrome, Firefox, Thunderbird use nssdb to work with certificates. You can import certificates both in the browser GUI and in the terminal using the certutil program.






































