-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
How to test the performance of a Linux server or PC
- Main
- Knowledge base
- How to test the performance of a Linux server or PC
Benchmarking programs help evaluate how fast your computer performs. For instance, if you've just built a new PC and want to test its performance after an upgrade, or if you're simply curious about how much faster (or slower) it is compared to a friend's or colleague's machine.
The easiest way to find out is by running a benchmark. In this article, we'll look at how to use the console-based benchmarking tool UnixBench.
How to Test Your PC with UnixBench
UnixBench is a traditional suite of tests designed for Unix-like systems. It has a long history, being a fork of the BYTE UNIX benchmark application first released back in 1983!
Although it's not the most modern solution, UnixBench is excellent for basic testing. It evaluates how well your computer handles tasks such as:
- working with 2D and 3D graphics;
- process creation;
- string operations;
- floating-point calculations;
- file copying, and more.
If you don't fully understand what these tests measure, that's okay. All you need to know is that UnixBench performs a stress test of the entire system (rather than individual components).
For Arch users, the utility is available through the AUR. For Ubuntu users, it can be installed via Snap.
Once installed, you can start the program by entering the command:
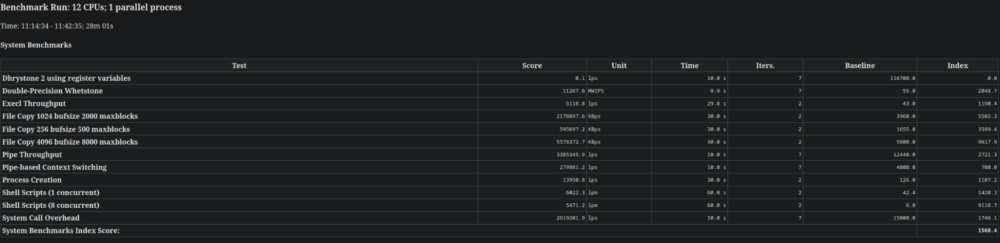
ubenchAs the test runs (and once it completes), you can navigate to the specified directory (/usr/lib/unixbench/results) to view the results. The results are available in both HTML and log file formats—choose whichever is most convenient for you.
If you need a quick way to evaluate the performance of your computer or server, UnixBench is an ideal choice. It's fast, resource-light, and provides results that are easy to compare with existing benchmarks available online.