-
Russia8 (800) 707-83-77
-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
How to add a script to Ubuntu autoloader
- Main
- Knowledge base
- How to add a script to Ubuntu autoloader
In some cases, it is necessary to execute your script when the system boots up. Such cases include the need to change the screen resolution, launch certain applications, and update a particular utility. Running a script can be accomplished in a variety of ways. You can do this by using a graphical shell or the systemd initialization system, which is now used in almost all distributions.
Autoloading by using the standard Ubuntu utility
The first thing to do is to create a script in a convenient location and execute it:
$ sudo gedit /script_path/script_name.sh
#!/bin/bash
echo "Hello world"This script will display "Hello world" messages to the user. Once the program is ready, it needs to be made executable. To do this, the following command is used:
$ sudo chmod ugo+x /script_path/script_name.shNext, in the main menu of the system, you need to launch the "Automatically Run Applications" utility.
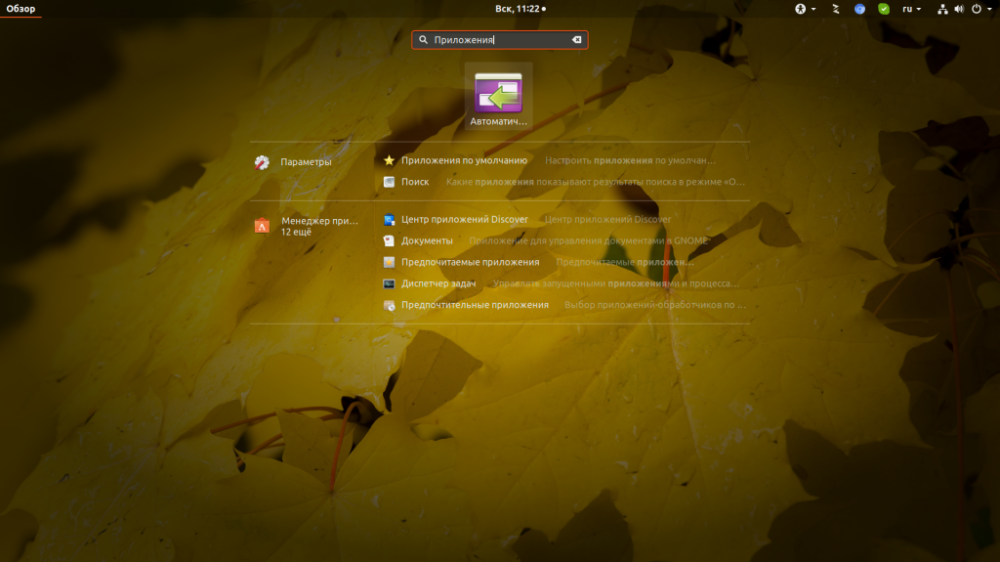
Click the "Add" button and enter the full path to the script file in the "Command" field. You can press the "Browse" button, find and select the script file and press "Add".
In the future, the program will be executed every time you start the Ubuntu graphical shell.
Autoload Linux scripts in Systemd
Use a special command to create a systemd service file
This is the command:
sudo systemctl edit --force myscript
You need to add the contents to this file:
[Unit]
Description=My Script Service
After=multi-user.target
[Service]
Type=idle
ExecStart=/full/path/to/script/script_name.sh
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target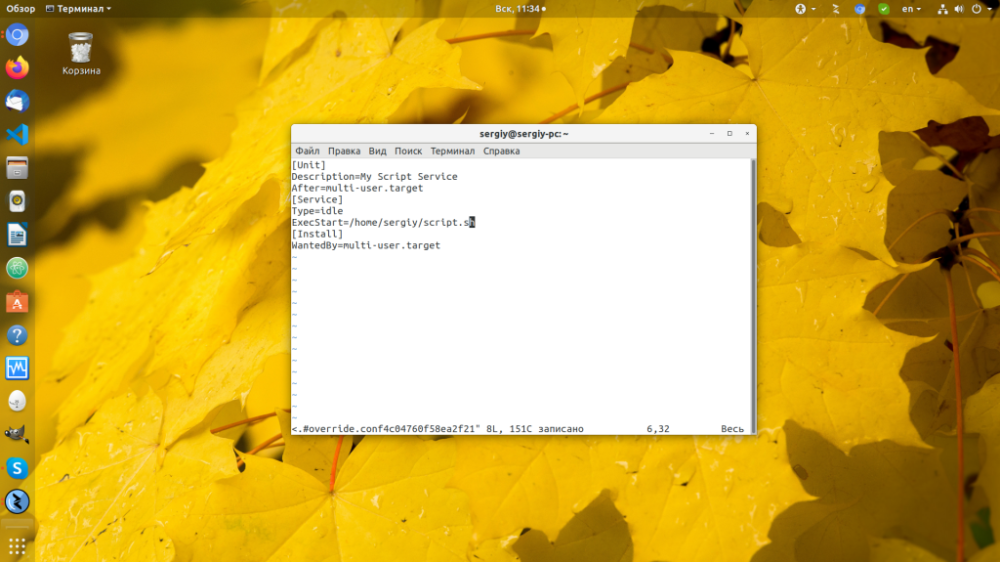
Next, in the line called ExecStart you need to fulfill one of the following requirements: write the path to the script or command to be executed. After that the script is added to the autoloader:
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl enable mysrciptThe program will start after system initialization. For this purpose, you can use the "old" method: you can use rc.local to create the file /etc/rc.local and write the path to it in the ExecStart line of the service file.






































