-
Russia8 (800) 707-83-77
-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
What you need to know about Inode in Linux
- Main
- Knowledge base
- What you need to know about Inode in Linux
An inode (Index Node) in Linux is a data structure that stores information about a file or directory, such as its owner, access rights, date and time of creation and modification, size, and location on the hard disk. Each file or directory in the system has its own unique index node number (inode number) that can be used to perform various operations on the file or directory. (inode number) that can be used to perform various operations on the file or directory.
What is an Inode in Linux
When you create a new file or directory in Linux, the file system allocates a new inode number for it and fills it with metadata. This inode number is unique for each file or directory in the file system and is used to identify the file or directory at the operating system kernel level.
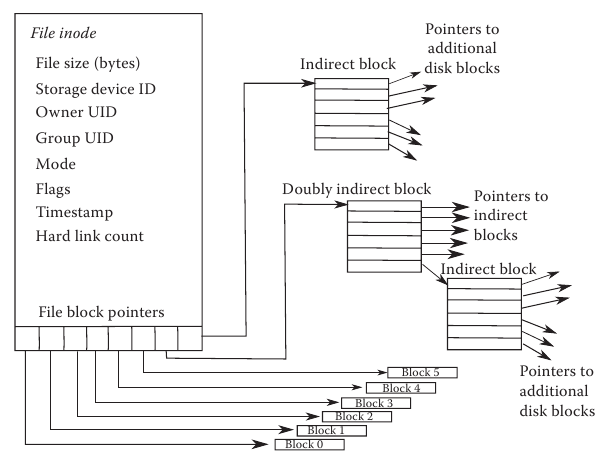
Inodes are limited in size, and therefore the number of files or directories that can be created in a file system is limited. However, file systems in Linux can use various strategies to increase the number of available inodes, such as creating file systems with a large number of inodes or using dynamic inode allocation.
Inodes are an important element of file systems in Linux, and knowing about them can be useful when working with files and directories at the system level, as well as when diagnosing and fixing file system problems.
What is important to know
If you are working with the Linux file system, you may find it useful to know the following about inode:
- Each file or directory in a file system has a unique inode number that identifies it at the operating system kernel level.
- The inode contains metadata about the file or directory, such as permissions, creation date and time, size, owner, group, and location of the file data on disk.
- Inodes have a limited size, so the number of files or directories that can be created on a file system is limited. The number of available inodes can be increased by creating file systems with more inodes or by using dynamic inode allocation.
- The use of inode can be useful when working with files and directories at the system level, especially if you need to perform operations that cannot be performed using normal file-level commands and operations.
- Knowledge of inode can be useful in diagnosing and fixing file system problems such as inode overflow, access errors, or file system corruption.
- Some Linux commands, such as
ls,df, andfind,can use inode to perform various file system-level operations. - It is important to realize that changing an inode can directly affect the file system and cause data loss, so you should be careful when working with inodes and only use them when it is necessary and you know what you are doing.
- Inodes are used in Linux file systems such as ext2, ext3, ext4, XFS, JFS and others. Each file system has its own ways of managing inodes and the maximum number of inodes that can be created on that file system.
- Inodes are also used to handle hard links in Linux. A hard link is a reference to a file that refers to the inode of that file, rather than to the file itself. As a result, hard links can point to the same file even if the file has different names and locations on the file system.
- If you want to know the number of free inodes on the file system, you can use the
dfcommand with the-ioption. For example, thedf -icommand will show the number of used and free inodes in each file system on your computer. - If you want to know the inode number for a particular file or directory, you can use the
lscommand with the-ioption. For example, the commandls -i myfile.txtwill show the inode number for the filemyfile.txt. - If you encounter file system problems that are inode related, you can use file system diagnostic tools such as fsck to fix the errors. However, you should back up your data before using such tools to avoid data loss.
Overall, understanding how inode works in Linux can be useful for working efficiently with files and directories at the system level, as well as for diagnosing and solving problems with file systems.
How to use inode
You can find out the inode number of a file or directory by using the ls command with the -i option:
$ ls -i filename.txt
1234567 filename.txtIn this example, "1234567" - is the inode number of the file filename.txt.
You can find files or directories by inode number by using the find command:
$ find / -inum 1234567$ find will find all files and directories on the system with inode number 1234567.
You can check how many inodes are occupied on a file system by using the df command with the -i option:
$ df -i
Filesystem Inodes IUsed IFree IUse% Mounted on
/dev/sda1 123456 65432 58024 53% /df -i will show information about the number of occupied and free inodes on the file system.
You can delete a file or directory by inode number by using the find command and the rm command:
$ find / -inum 1234567 -exec rm {} ;$ find will find the file or directory with inode number 1234567 and delete it.
The use of inode in Linux can be useful when working with files and directories at the system level, especially if you need to perform operations that cannot be performed with normal commands and file-level operations.






































