-
Russia8 (800) 707-83-77
-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
What the pwd command does in Linux
- Main
- Knowledge base
- What the pwd command does in Linux
This is a very simple utility that allows you to display the path to the current folder in the terminal. At startup each program gets the current folder, where all operations with files of this program will take place, if no other path is specified. Relative paths will also be counted from this folder. Thus, when the terminal is launched, the current folder becomes the user's home directory. If a program is launched from a specific folder, then by default its current folder will be the directory from which it was launched.
What the pwd command does in Linux
The command has a fairly simple syntax:
$ pwd опцииIn order to customize the output of the utility, the user can use the following options:
-L, --logical- take the directory from the environment variable, even if it contains symbolic links;-P- discard all symbolic links;--help- display utility help;--version- display the utility version.
Now let's consider some examples of working with this command in the Linux operating system. To view the current Linux folder it is enough to execute pwd without parameters:
$ pwd 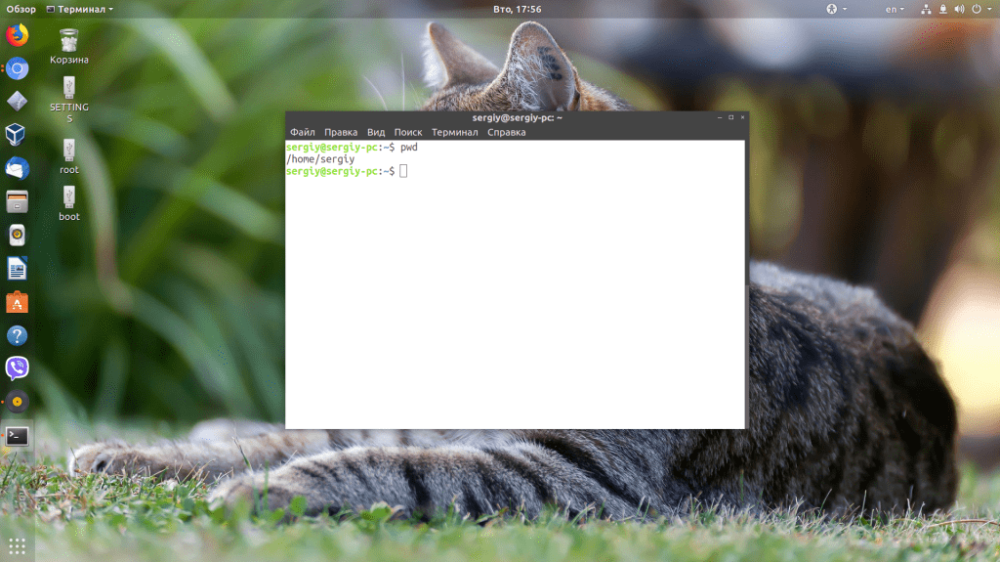
The command has the -P option, due to which it manages to discard all symbolic links. This is useful when there are symbolic links along the path to the current folder. The command will simply specify the full path without symbolic links. It looks like this:
$ pwd -P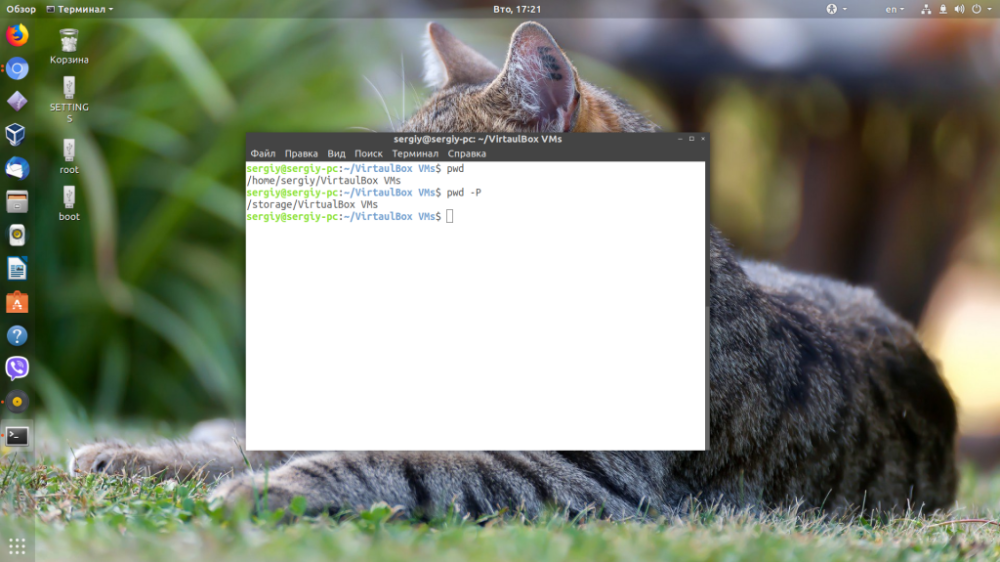 Often in command interpreters,
Often in command interpreters, pwd comes as a built-in command. This means that the interpreter does not need to call a third-party utility, so the code executes very quickly.
To find out the current folder, you don't need to call the script, you just need to call the PWD environment variable.
$echo $PWD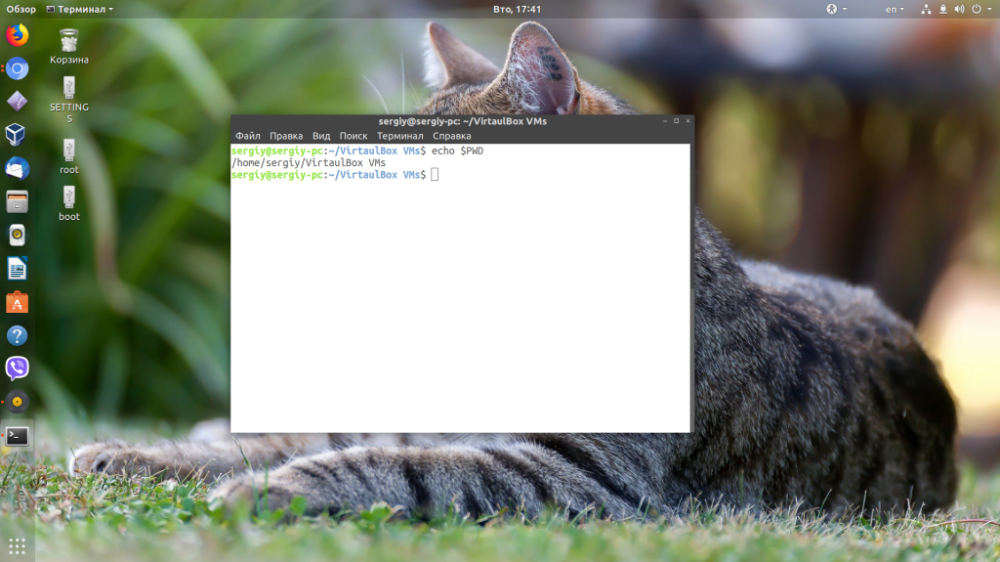
To write the result of the pwd linux command to a variable, execute:
$CWD=$(pwd)
$echo $CWD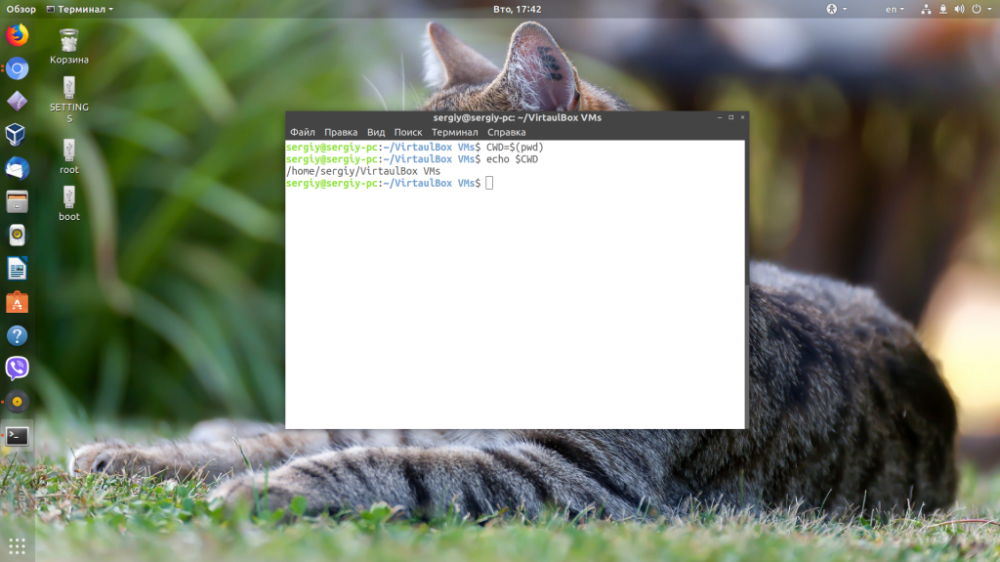
The pwd command is rarely used in Linux, however, if you need to change the current folder you can use it. As you can see from the example, it is not that hard to do.






































