-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Du command in Linux
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Du command in Linux
In some cases, you may need to see how much space files take up in a particular folder and find the largest files to delete. There are several tools to solve these tasks, but the simplest of them is the du utility. It allows you to display the size of all files in a certain folder in bytes or in a more convenient format. Let's see what the du Linux command is and how to use it to solve your work tasks.
Command options
The syntax is simple. It is enough to pass options and path to the folder you want to work with:
$ du options /path/to/folderUtility Options:
-a,--alloutput the size for all files, not just directories, by default it is output only for folders;-B,--block-sizespecify the size output units, available: K,M,G,T,P,E,Z,Y for 1024 and KB, MB and so on for 1000;-c,--totaloutput the total size of all folders at the end;-d,--max-depthmaximum directory nesting depth;-h,--human-readableoutput the size in human-friendly units;--inodes- output information about inode usage;-L,--dereference- to follow all symbolic links;-l,--count-links- consider the file size multiple times for hard links;-P,--no-dereference- not to follow symbolic links, this is the default behavior;-S,--separate-dirs- Do not include the size of subfolders in the folder size;--si- выводить размер файлов и папок в системе си, используется 1000 вместо 1024;-s,--summarize- output only the total size;-t,--threshold- do not consider files and folders with a size smaller than the specified size;--time- display the last modification time for a file or folder, instead of modification time you can display the following labels: atime, access, use, ctime;-X,--exclude- to exclude files from the count;-x,--one-file-system- skip mounted file systems;--version- display the version of the utility.
To view all options, follow the steps below:
How do I use the command?
To simply display a list of folders in a particular directory and the space they occupy, e.g. in /var, run:
$ man dIf you want the size to be displayed in a more readable form, use the option-h:
$ du -h /var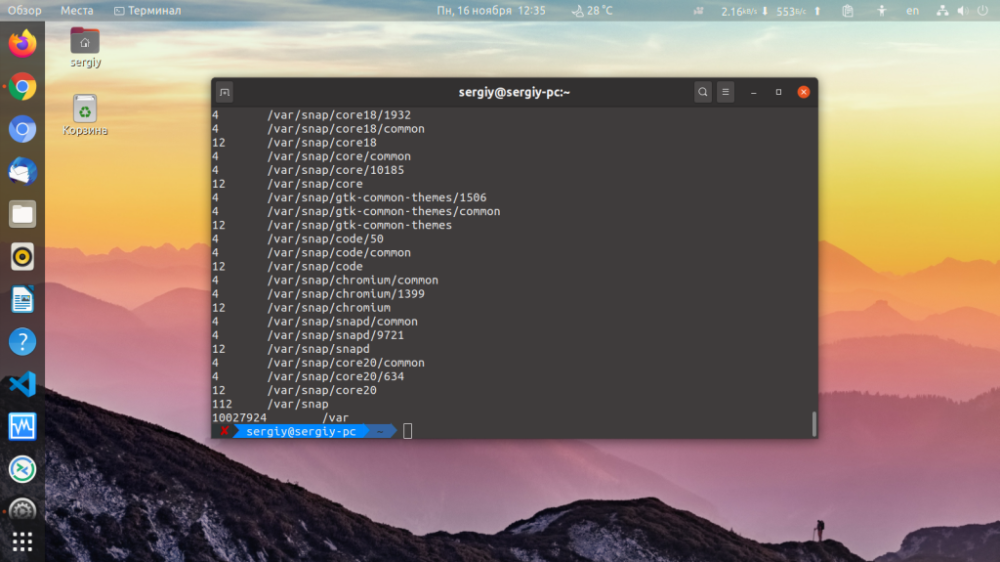
You can also specify the block size. Then the accuracy will be a bit lower because the minimum unit of measure is one block. For example, to output the size of folders in megabytes with a 1024 kilobyte block, use the -B option with the M parameter:
$ du -BM /var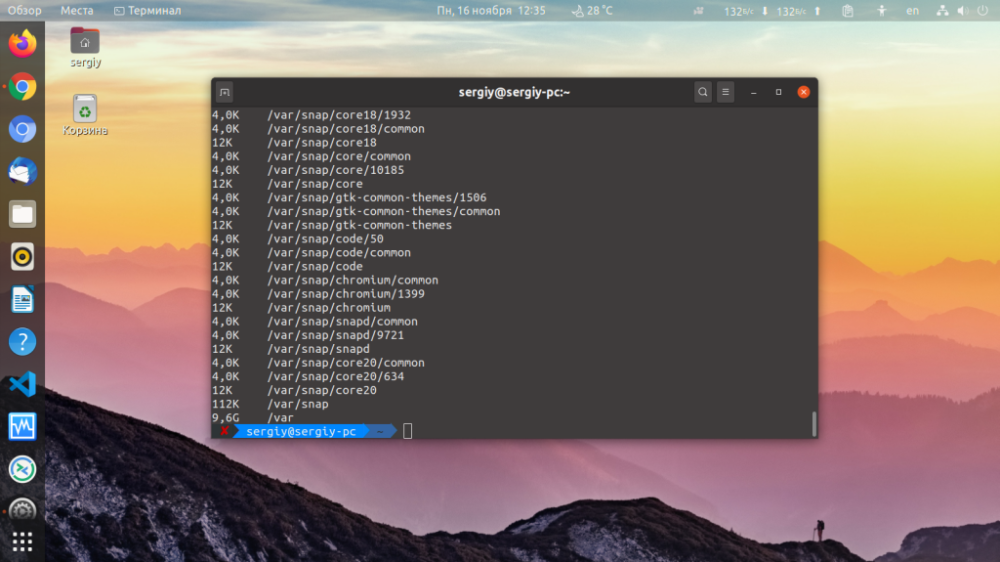
You can display not only the size of folders, but also the size of files that are located there, use the option -a:
$ du -BM /var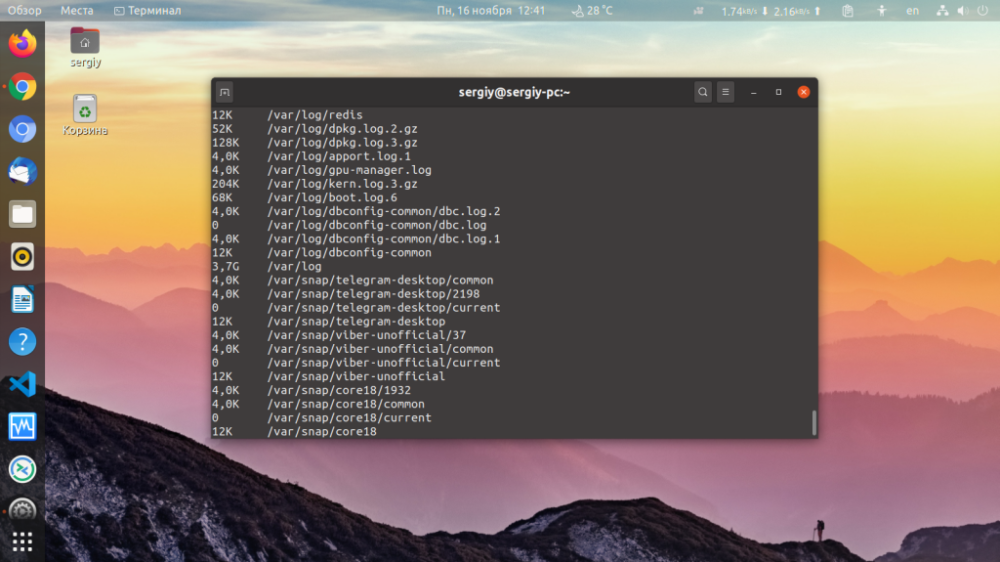
To display only the total size of all files and folders you need to apply the option -s:
$ du -BM /varWhen it is necessary to display the size of folders without subfolders, use the option -m:
$ du -BM /var
There is also an option to display a line with the total size of the entire folder. But it is advisable to use this feature with the option -S:
$ du -hSc /va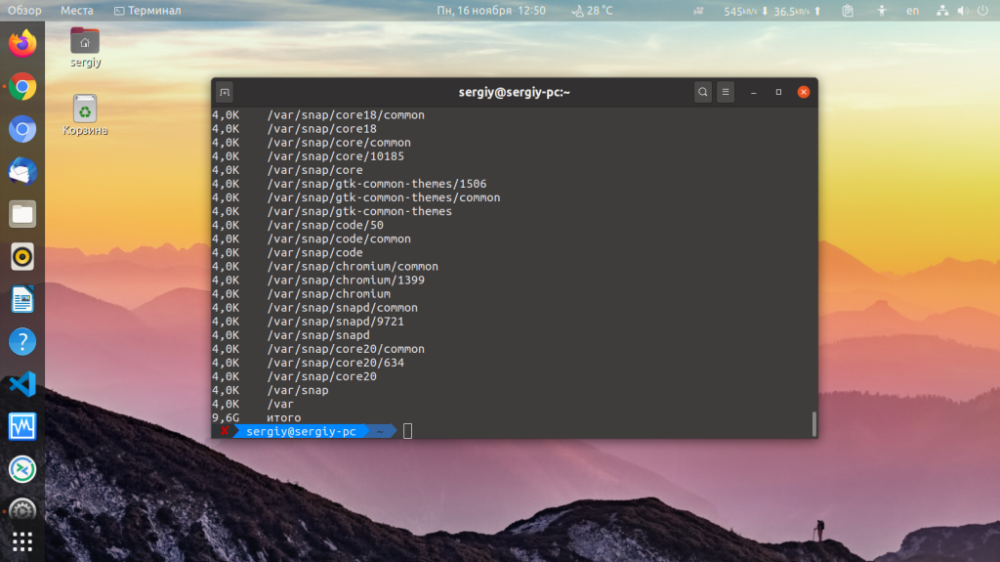
To eliminate everything in the log:
$ du -hac --exclude="*.log"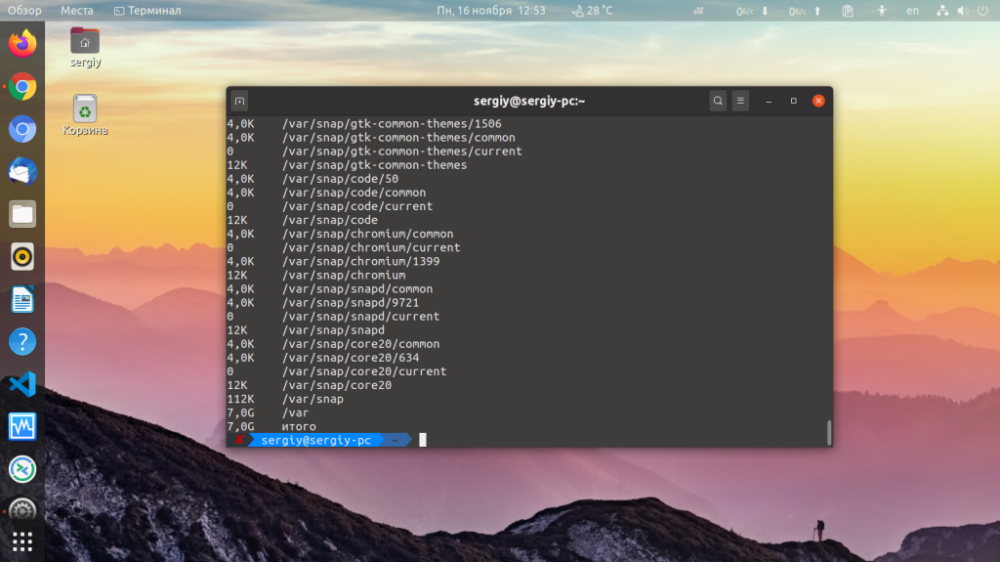
To sort values in a convenient format:
$ du -hac --exclude="*.log"






































