-
United Kingdom+44 (20) 4577-20-00
-
USA+1 (929) 431-18-18
-
Israel+972 (55) 507-70-81
-
Brazil+55 (61) 3772-18-88
-
Canada+1 (416) 850-13-33
-
Czech Republic+420 (736) 353-668
-
Estonia+372 (53) 683-380
-
Greece+30 (800) 000-02-04
-
Ireland+353 (1) 699-43-88
-
Iceland+354 (53) 952-99
-
Lithuania+370 (700) 660-08
-
Netherlands+31 (970) 1027-77-87
-
Portugal+351 (800) 180-09-04
-
Romania+40 (376) 300-641
-
Sweden+46 (79) 008-11-99
-
Slovakia+421 (2) 333-004-23
-
Switzerland+41 (22) 508-77-76
-
Moldova+373 (699) 33-1-22
 English
English
Changing user password in MySQL
- Main
- Knowledge base
- Changing user password in MySQL
When working with MySQL DBMS, it is extremely important to know how to change the user password. It seems that this task can be solved only if you have superuser rights. But even an ordinary user can change the password under certain circumstances. In this article, we will tell you how to do it under normal circumstances.
Changing the user password in MySQL DBMS
You can change a user's password in different ways. In the MySQL environment, there are two commands for this task - SET PASSWORD and ALTER USER. Let's tell you about each of these two methods in detail.
Let's find out the MySQL version
At the beginning of this year, MySQL has two major versions. The first one is outdated but still supported (it is version 5.7), and the most current one at the moment is version 8.0. How to find out the MySQL version? You can do this with a special command that should be executed in the terminal:
$ mysql –version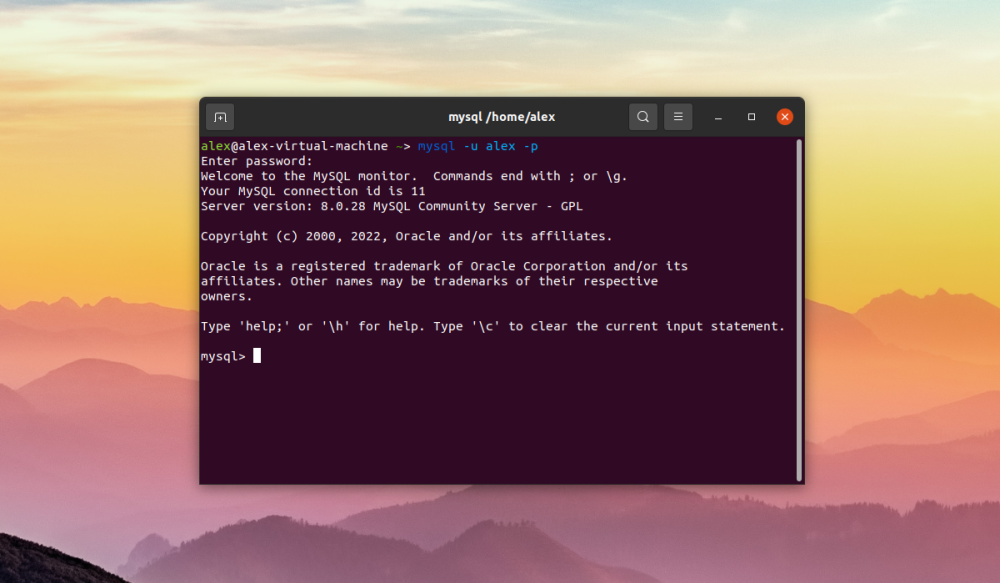
As you can see from the image above, version 8.0.28 is used, but it is important to take into account that ALTER USER is relevant only in previous versions of MySQL.In newer versions, you can use both versions.
How to enter the console
To enter the console, you should be authorized in MySQL using your login and password. When a user is already authorized on the server, you should perform all actions on his behalf. In the case when MySQL is used for the first time, you should use root privileges.
The command to log in as root:
$ mysql -u root –p
After that, a password prompt will occur. It remains to enter the password, press Enter, immediately after that the MySQL interface with all available commands will be loaded.
Viewing hosts
The peculiarity of MySQL is that it has a separate host to which an account is bound. Let's note the three main hosts:
- Localhost;
- %;
- IP address/domain name.
Localhost allows only local login with no remote connectivity, % means that the account can be used from any host, IP address/domain name means that the account can only be used at the selected domain name/IP address.
To find out the host type of the account we need to run the following SQL query:
$ SELECT user, host FROM mysql.user
In the screenshot above, we can see that for user alex the host % is involved. This host should be used when changing the password. Users in MySQL and all information about users are stored in mysql database in the table user.
Changing the password using SET PASSWORD
You can also change the password with the SET PASSWORD command. To change the password for user alex with host % to somepassword666 you need to use the following command:
$ SET PASSWORD FOR 'alex'@'%' = 'somepassword666';
Changing the password using ALTER USER
You can change the user code using another command - ALTER USER. To change the password for the user alex with host % to anotherpassword666 we will execute a SQL query:
$ ALTER USER 'alex'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY 'anotherpassword666';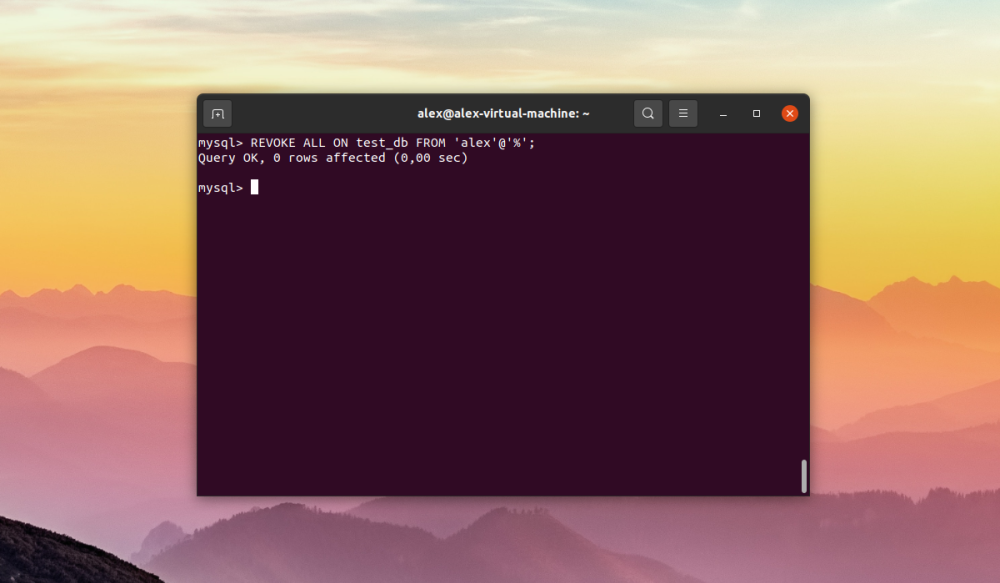
Here we should take into account that username and user host are enclosed in single quotes, without these quotes MySQL will not be able to recognize the string.
Now reset the privilege cache:
$ FLUSH PRIVILEGES;How to verify the new password
Once you have changed the password, changed the privilege and reset the cache, you should perform a login verification as the user whose password was changed.
Exit the MySQL shell by executing the exit command:
$ exit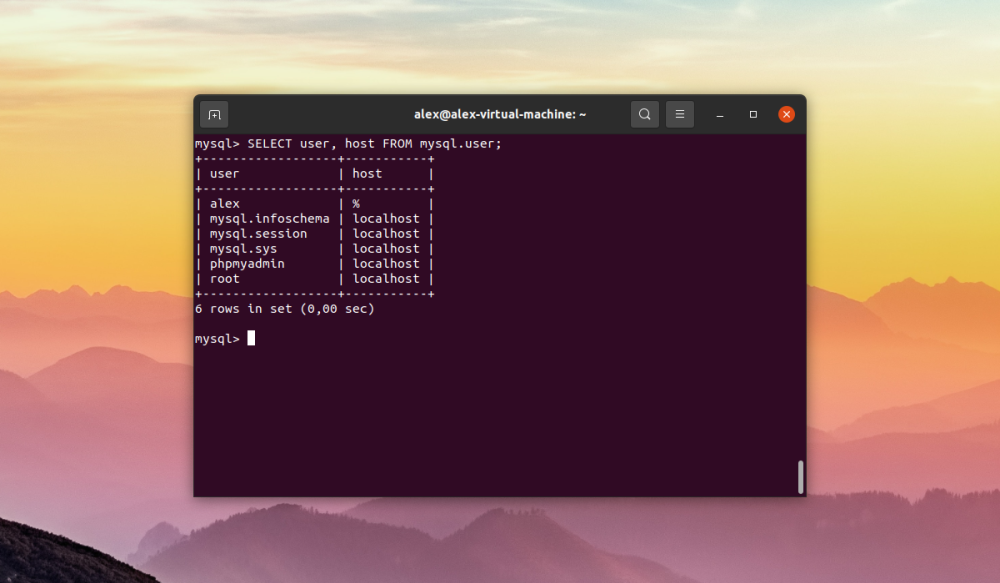
Now log in to the shell:
$ mysql -u alex -p
If you see the system prompt while logging in, you did everything correctly, which means that the password was successfully changed.






































